Opinion
Quo Vadis Sri Lanka Tourism, Post Covid-19?
By Srilal Miththapala
There seems to be conflicting ideas as to how tourism should be promoted in the short term, in the post Covid -19 arena. A wide range of good initiatives have been proposed from various experts. We must not get carried away by emotion, and resort to ‘crystal ball gazing’, but make our plans, based on evidence and research.
What seems to be overlooked is the need to properly understand the post Covid-19 consumer behaviour, and only focus source markets. Finally, it is the consumer who will decide, whoever he may be.
The bottom line is that the ‘tourism world’ is not going to come back to normal for quite some time. Like everything else in our lives, consumers also will respond in a ‘new normal’ framework. Hence applying our traditional marketing strategies will not necessarily work in this uncertain environment. Many may accuse me of being a pessimist. But I would like to be understood as a pragmatist.
This essay will try to analyse the consumer mind set in the post CoVid-19 scenario, and then try to develop what marketing strategies would work to match these consumer needs.

1.0 Introduction
The coronavirus crisis is having massive impacts on the tourism industry—many of which will reshape the industry’s future landscape. What actions should the stakeholders of this industry be taking today from a marketing and communications perspective? The truth is no one knows for sure. We are all in the dark. However, a business-as-usual approach is almost certainly wrong because there is nothing “usual” about this new life we’re all living and what’s happening to the tourism industry right now.
Just when the crisis seemed to be abating, we are now hit by a new variant of the virus that could have more disastrous impact. However, initial reports indicate that although it could be more infections than the Delta strain, the severity of the illness is probably less severe. It is still uncertain how different countries will respond to this new challenge.
2.0 Tourism Recovery
A recent global survey of UNWTO tourism experts on the recovery of travel shows a slight increase in confidence with 60 percent of consumers saying they expect to see a rebound in international tourism by 2022, versus just 50 percent in an earlier January 2021 survey.
In spite of this slight boost in confidence, nearly half of the respondents said that they did not expect international tourism to return to 2019 levels until 2024 or later. Similarly, 37 percent fewer respondents now believe 2023 could be the full recovery year.
In another study by Deloitte’s for Australia Tourism, there were three different scenarios presented.
Mild (best case) – international arrivals return to 2019 level by 2022.
Harsh (probable) – International tourist arrivals return to 2019 level by 2023.
Severe (worst case) – International arrivals return to 2019 level by 2025.
Boston Consulting Group predicts that travel won’t rebound to 2019 levels until 2023 or 2024. “The tourism business is driven by the great intangible of consumer confidence. Regardless of therapeutics or vaccine availability, second or third waves, or the efficacy of safety protocols, the industry won’t fully recover until travellers and service providers do so psychologically.”
Hence most studies indicate that it will be 2023 by the time tourism recovers to pre Covid-19 levels.
(it must be noted that all such studies were done before the new Omicron outbreak and how that is going to impact consumer sentiment is still to be seen.)
To expect arrival numbers to reach the pre Covid-19 of about 100,000 – 150,000 per month in the next 12 months in Sri Lanka is a pipe dream. (We have just reached 100,000 arrivals for the year, only about 7% of pre Covid-19 days)
Hence, its high time that stakeholders accept that full recovery of tourism is going to be another 12-18 months away.
Tourism professionals should take cognisance of this, and plan for it. They should adjust their strategies, accordingly, to survive and make the best of the situation in the short term. This does not mean that there will be no tourism in 2021. Certainly, there will be, and what will follow in this essay, is to try and understand the consumer mind-set of these travellers, who would venture out in spite of certain uncertainties.
(TTRW: MADRID, 2 December 2021: One out of five destinations continue to have their borders completely closed as new surges of Covid-19 impact the restart of international tourism, while the WHO declaration identifying Omicron as a variant of concern will prompt additional restrictions.
The latest UNWTO research shows that still 98% of all destinations have some travel restrictions in place.)
3.0 Marketing in the short term after Covid-19
It is needless to say that under such circumstances where survival would be the focus, positioning and branding will have to take a back seat. But that does not mean to say that planning should stop. The time could be spent by all stakeholders to properly develop a positioning for the country and to ‘extract out’ what our real USP is. At a recent webinar I heard suggestions for a whole range of ‘unique propositions’ from cultural pageants, wildlife, nature, environment, food, wellness, ‘experience,’ etc. (there is a misnomer in considering ‘experience’ as a category. It is true that most tourists pay great emphasis on experience. But the ‘experience’ should cut across every category, be it wild life, wellness or food).
Obviously, Sri Lanka as a destination cannot be ‘everything for everyone’. Sometimes I think this blessing of a range of natural attractions, is Sri Lanka tourism’s problem. We have too much! Because we are blessed with a plethora of natural beauty and attractions, it’s easy to be carried away, and try to promote everything. It is my humble opinion that even launching the muchtalked- about Global Campaign is not advisable at this time. It is true that we have waited a long time for this. But is the market ready for it at this juncture?
The need of the hour is a short-term push marketing initiative, to ‘push’ the product and service attributes of Sri Lanka that will appeal to the prospective travellers in this uncertain market environment. The ‘pull’ marketing strategy, whereby we reach out to travellers with our brand attributes and unique propositions to create new customers, should follow thereafter, once some form of proper and consistent normalcy has arrived.
So the priority in the short term is the need for a strong communication programme to reach out to the smaller, specific segments of consumers who would consider traveling in next 12-18 months.
The ‘tourism cake’ has shrunk. And everyone (all tourism destinations) are trying to get a share.
So how does Sri Lanka reach out and get a bigger share of this cake?
4.0 The need for evidence-based decision-making.
SL tourism has never given too much prominence to research and evidence-based decision-making. I guess it is no surprise when the leadership of the whole country depends on soothsayers and astrologers and quack–brewed concoctions to rid the CoVid19 virus, while the sane voices of the professionals are given a deaf ear.
But then again tourism is such an interesting subject that everyone from streetside vendors to desk-based government bureaucrats and inexperienced and clueless ministers, are experts on the subject. Even tourism professionals tend to lean on their old experiences and emotions, rather than, on good research. The need for a private -public sector partnered tourism research unit has been talked about ad nauseam. (I myself have presented many proposals for such an initiative over the past years.)
The crying need of the hour (and of course in the long term as well) is to have good reliable feedback about the tourism market. Would it be difficult to interview the few tourists who are coming to Sri Lanka at the airport? Why did they decide to travel? Why did they choose Sri Lanka? Were they satisfied with their stay?, etc.
Such simple questions will give feedack which will be so useful to tweak our offering and to be more focused on our future promotional efforts. The importance should be on the return on every dollar spent on promotion in these difficult times, and not on the value of the promotion.
5.0 Short Term ‘Push’ Marketing –
Segmentation
In trying to develop such a communication plan, (I use the word plan and not strategy since it is short term oriented) the first focus should be on the tourism consumer. One way to segment the traveller would be based on mind-set.
5.1 The Potential
travellers.
The possible consumer segments in the immediate post-Covid-19 era and their general characteristics could be as follows-
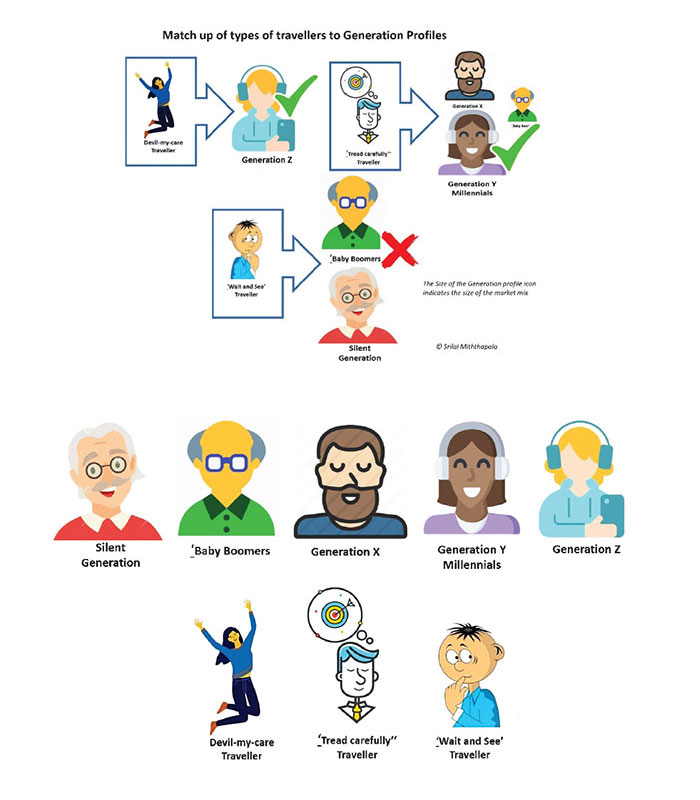
‘Devil may care’ traveller
The impetuous, young, adventurous risk takers. Not concerned about pandemic. Possibly with limited financial resources. (The conventional backpackers would also fall into this category but their monetary standing, post- CoVid-19 may be wanting)
‘Tread carefully’‘ traveller
Earns to travel. Will check all pros and cons on social media and other media channels and make careful decisions about travelling. Possibly young/middle aged, well-educated with adequate disposable income.
‘Wait and See’ traveller
Ultra-safety conscious and anxious about travelling. Possibly middle aged or Senior citizens, families with young children. Adequate financial resources.
It is evident that the segment who would travel under current prevailing circumstances would be predominately the ‘Devil-may-care’ Traveller, and to a lesser degree the ‘Tread carefully’ traveller segment. It will be quite a while before the ‘Wait and see’ traveller ventures out, and therefore there is no point in spending resources in engaging that category.
Hence it is not rocket science to conclude that a short term push marketing initiative must be specifically targeted at these two segments.
5.2 The Generic Consumer segments (Generational profiling)
The usually accepted generic consumer demographic segments are-
Silent Generation -Born 1925-1945; Current Ave. age 80’s- Small size
= Hard working
=Conservative
= Healthy, and most educated
= Wealthiest generation
Baby Boomers – Born 1945-1960; Current Ave. age 70’s-Medium size
= Larger families
= Non traditional
= Physically fit
= Wealthy
= Leisure activities
Generation X –Born 1960-1980; Current Ave. age 50’s-Large size
= Enjoy creative input and resourceful
= Embrace technology and social media
= Strong emphasis on family time and work-life balance
= Hard working
= Financially well off
= Comfortable with technology
Generation Y (Millennials)-Born 1980-1990; Current Ave. age 30’s-Large size
= Diverse
= Impatient
= Creative
= Multi-taskers
= Internet and social media part of their lives
= Reasonably wealthy
Generation Z – Born 1990-present; Current Ave. age< 30’s- Medium size
= Self-reliant
= Risk takers
= Can be suspicious of larger corporations
= Not too brand loyal
= Short span of interest
=Fully ‘wired’ almost always
= Reliant on social media platforms
= Very concerned about environment, ethics and social wellbeing of people
Although this categorisation is predominantly relevant to developed countries, with globalisation and the spread of the internet, it is valid for most emerging countries as well.
The types of traveller identified earlier can now be matched with the generation profile characterises to help target the required segment, with an appropriate and relevant commination initiative.
This indicates that the market segments most likely to travel in the short term are
Gen Z (medium size)
Gen Y (large size)
Gen X –to a lesser extent (Large size)
6.0 Short Term ‘Push’ Marketing- The Communication
So how do you reach out to the Generation Z’s and Y’s ?
The answer is to study their inherent characteristics, and respond accordingly to what motivates them.
The platform must necessary be digital.
The medium must be internet based. Social media, blogs, etc. (Brochures, print media and trade fairs will not work. Even Facebook is outdated)
The message should be based around-
= Health and Safety. ( this will be of paramount importance to all segments)
= Short and sweet, to the point
= Authentic and reliable
= Personalised, small scale programs
= Meaningful stories
= More pictures & Videos
= Highlight social and community benefits
= Ethical travel themes
= Travel for a cause
= Environment, outdoor,
= Nature and wildlife
= Off the beaten track
= Wellness and meditation/yoga
Hence once an analytical approach is taken to identify key market segments based on demographics it will be easier to target the desired travellers with a cost effective communications programme.
6.0 Conclusion
In the foregoing I have attempted to show how an analytical approach based on good consumer data, could be, designed and implemented. This is by no means a perfect model, and is presented only as an example. Professional markers will be able to design more comprehensive initiatives. The important fact is that needs to be highlighted is that we must break out of our shackles of being the ‘know-it-all s’ and reach out to good research and information to base our plans on.
Otherwise, Sri Lanka Tourism will continue to blunder around with its’ sawn off double-barrelled shot gun, spraying bullets all over, hitting only a rare target or two’.
Opinion
Child food poverty: A prowling menace

 by Dr B.J.C.Perera
by Dr B.J.C.Perera
MBBS(Cey), DCH(Cey), DCH(Eng), MD(Paed), MRCP(UK), FRCP(Edin),
FRCP(Lon), FRCPCH(UK), FSLCPaed, FCCP, Hony FRCPCH(UK), Hony. FCGP(SL)
Specialist Consultant Paediatrician and Honorary Senior Fellow,
Postgraduate Institute of Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka.
Joint Editor, Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health
In an age of unprecedented global development, technological advancements, universal connectivity, and improvements in living standards in many areas of the world, it is a very dark irony that child food poverty remains a pressing issue. UNICEF defines child food poverty as children’s inability to access and consume a nutritious and diverse diet in early childhood. Despite the planet Earth’s undisputed capacity to produce enough food to nourish everyone, millions of children still go hungry each day. We desperately need to explore the multifaceted deleterious effects of child food poverty, on physical health, cognitive development, emotional well-being, and societal impacts and then try to formulate a road map to alleviate its deleterious effects.
Every day, right across the world, millions of parents and families are struggling to provide nutritious and diverse foods that young children desperately need to reach their full potential. Growing inequities, conflict, and climate crises, combined with rising food prices, the overabundance of unhealthy foods, harmful food marketing strategies and poor child-feeding practices, are condemning millions of children to child food poverty.
In a communique dated 06th June 2024, UNICEF reports that globally, 1 in 4 children; approximately 181 million under the age of five, live in severe child food poverty, defined as consuming at most, two of eight food groups in early childhood. These children are up to 50 per cent more likely to suffer from life-threatening malnutrition. Child Food Poverty: Nutrition Deprivation in Early Childhood – the third issue of UNICEF’s flagship Child Nutrition Report – highlights that millions of young children are unable to access and consume the nutritious and diverse diets that are essential for their growth and development in early childhood and beyond.
It is highlighted in the report that four out of five children experiencing severe child food poverty are fed only breastmilk or just some other milk and/or a starchy staple, such as maize, rice or wheat. Less than 10 per cent of these children are fed fruits and vegetables and less than 5 per cent are fed nutrient-dense foods such as eggs, fish, poultry, or meat. These are horrendous statistics that should pull at the heartstrings of the discerning populace of this world.
The report also identifies the drivers of child food poverty. Strikingly, though 46 per cent of all cases of severe child food poverty are among poor households where income poverty is likely to be a major driver, 54 per cent live in relatively wealthier households, among whom poor food environments and feeding practices are the main drivers of food poverty in early childhood.
One of the most immediate and visible effects of child food poverty is its detrimental impact on physical health. Malnutrition, which can result from both insufficient calorie intake and lack of essential nutrients, is a prevalent consequence. Chronic undernourishment during formative years leads to stunted growth, weakened immune systems, and increased susceptibility to infections and diseases. Children who do not receive adequate nutrition are more likely to suffer from conditions such as anaemia, rickets, and developmental delays.
Moreover, the lack of proper nutrition can have long-term health consequences. Malnourished children are at a higher risk of developing chronic illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity later in life. The paradox of child food poverty is that it can lead to both undernutrition and overnutrition, with children in food-insecure households often consuming calorie-dense but nutrient-poor foods due to economic constraints. This dietary pattern increases the risk of obesity, creating a vicious cycle of poor health outcomes.
The impacts of child food poverty extend beyond physical health, severely affecting cognitive development and educational attainment. Adequate nutrition is crucial for brain development, particularly in the early years of life. Malnutrition can impair cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and problem-solving skills. Studies have consistently shown that malnourished children perform worse academically compared to their well-nourished peers. Inadequate nutrition during early childhood can lead to reduced school readiness and lower IQ scores. These children often struggle to concentrate in school, miss more days due to illness, and have lower overall academic performance. This educational disadvantage perpetuates the cycle of poverty, as lower educational attainment reduces future employment opportunities and earning potential.
The emotional and psychological effects of child food poverty are profound and are often overlooked. Food insecurity creates a constant state of stress and anxiety for both children and their families. The uncertainty of not knowing when or where the next meal will come from can lead to feelings of helplessness and despair. Children in food-insecure households are more likely to experience behavioural problems, including hyperactivity, aggression, and withdrawal. The stigma associated with poverty and hunger can further exacerbate these emotional challenges. Children who experience food poverty may feel shame and embarrassment, leading to social isolation and reduced self-esteem. This psychological toll can have lasting effects, contributing to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety in adolescence and adulthood.
Child food poverty also perpetuates cycles of poverty and inequality. Children who grow up in food-insecure households are more likely to remain in poverty as adults, continuing the intergenerational transmission of disadvantage. This cycle of poverty exacerbates social disparities, contributing to increased crime rates, reduced social cohesion, and greater reliance on social welfare programmes. The repercussions of child food poverty ripple through society, creating economic and social challenges that affect everyone. The healthcare costs associated with treating malnutrition-related illnesses and chronic diseases are substantial. Additionally, the educational deficits linked to child food poverty result in a less skilled workforce, which hampers economic growth and productivity.
Addressing child food poverty requires a multi-faceted approach that tackles both immediate needs and underlying causes. Policy interventions are crucial in ensuring that all children have access to adequate nutrition. This can include expanding social safety nets, such as food assistance programmes and school meal initiatives, as well as targeted manoeuvres to reach more vulnerable families. Ensuring that these programmes are adequately funded and effectively implemented is essential for their success.
In addition to direct food assistance, broader economic and social policies are needed to address the root causes of poverty. This includes efforts to increase household incomes through living wage policies, job training programs, and economic development initiatives. Supporting families with affordable childcare, healthcare, and housing can also alleviate some of the financial pressures that contribute to food insecurity.
Community-based initiatives play a vital role in combating child food poverty. Local food banks, community gardens, and nutrition education programmes can help provide immediate relief and promote long-term food security. Collaborative efforts between government, non-profits, and the private sector are necessary to create sustainable solutions.
Child food poverty is a profound and inescapable issue with far-reaching consequences. Its deleterious effects on physical health, cognitive development, emotional well-being, and societal stability underscore the urgent need for comprehensive action. As we strive for a more equitable and just world, addressing child food poverty must be a priority. By ensuring that all children have access to adequate nutrition, we can lay the foundation for a healthier, more prosperous future for individuals and society as a whole. The fight against child food poverty is not just a moral imperative but an investment in our collective future. Healthy, well-nourished children are more likely to grow into productive, contributing members of society. The benefits of addressing this issue extend beyond individual well-being, enhancing economic stability and social harmony. It is incumbent upon us all to recognize and act upon the understanding that every child deserves the right to adequate nutrition and the opportunity to thrive.
Despite all of these existent challenges, it is very definitely possible to end child food poverty. The world needs targeted interventions to transform food, health, and social protection systems, and also take steps to strengthen data systems to track progress in reducing child food poverty. All these manoeuvres must comprise a concerted effort towards making nutritious and diverse diets accessible and affordable to all. We need to call for child food poverty reduction to be recognized as a metric of success towards achieving global and national nutrition and development goals.
Material from UNICEF reports and AI assistance are acknowledged.
Opinion
Do opinion polls matter?

By Dr Upul Wijayawardhana
The colossal failure of not a single opinion poll predicting accurately the result of the Indian parliamentary election, the greatest exercise in democracy in the world, raises the question whether the importance of opinion polls is vastly exaggerated. During elections two types of opinion polls are conducted; one based on intentions to vote, published during or before the campaign, often being not very accurate as these are subject to many variables but exit polls, done after the voting where a sample tally of how the voters actually voted, are mostly accurate. However, of the 15 exit polls published soon after all the votes were cast in the massive Indian election, 13 vastly overpredicted the number of seats Modi’s BJP led coalition NDA would obtain, some giving a figure as high as 400, the number Modi claimed he is aiming for. The other two polls grossly underestimated predicting a hung parliament. The actual result is that NDA passed the threshold of 272 comfortably, there being no landslide. BJP by itself was not able to cross the threshold, a significant setback for an overconfident Mody! Whether this would result in less excesses on the part of Modi, like Muslim-bashing, remains to be seen. Anyway, the statement issued by BJP that they would be investigating the reasons for failure rather than blaming the process speaks very highly of the maturity of the democratic process in India.
I was intrigued by this failure of opinion polls as this differs dramatically from opinion polls in the UK. I never failed to watch ‘Election night specials’ on BBC; as the Big Ben strikes ‘ten’ (In the UK polls close at 10pm} the anchor comes out with “Exit polls predict that …” and the actual outcome is often almost as predicted. However, many a time opinion polls conducted during the campaign have got the predictions wrong. There are many explanations for this.
An opinion poll is defined as a research survey of public opinion from a particular sample, the origin of which can be traced back to the 1824 US presidential election, when two local newspapers in North Carolina and Delaware predicted the victory of Andrew Jackson but the sample was local. First national survey was done in 1916 by the magazine, Literary Digest, partly for circulation-raising, by mailing millions of postcards and counting the returns. Of course, this was not very scientific though it accurately predicted the election of Woodrow Wilson.
Since then, opinion polls have grown in extent and complexity with scientific methodology improving the outcome of predictions not only in elections but also in market research. As a result, some of these organisations have become big businesses. For instance, YouGov, an internet-based organisation co-founded by the Iraqi-born British politician Nadim Zahawi, based in London had a revenue of 258 million GBP in 2023.
In Sri Lanka, opinion polls seem to be conducted by only one organisation which, by itself, is a disadvantage, as pooled data from surveys conducted by many are more likely to reflect the true situation. Irrespective of the degree of accuracy, politicians seem to be dependent on the available data which lend explanations to the behaviour of some.
The Institute for Health Policy’s (IHP) Sri Lanka Opinion Tracker Survey has been tracking the voting intentions for the likely candidates for the Presidential election. At one stage the NPP/JVP leader AKD was getting a figure over 50%. This together with some degree of international acceptance made the JVP behave as if they are already in power, leading to some incidents where their true colour was showing.
The comments made by a prominent member of the JVP who claimed that the JVP killed only the riff-raff, raised many questions, in addition to being a total insult to many innocents killed by them including my uncle. Do they have the authority to do so? Do extra-judicial killings continue to be JVP policy? Do they consider anyone who disagrees with them riff-raff? Will they kill them simply because they do not comply like one of my admired teachers, Dr Gladys Jayawardena who was considered riff-raff because she, as the Chairman of the State Pharmaceutical Corporation, arranged to buy drugs cheaper from India? Is it not the height of hypocrisy that AKD is now boasting of his ties to India?
Another big-wig comes with the grand idea of devolving law and order to village level. As stated very strongly, in the editorial “Pledges and reality” (The Island, 20 May) is this what they intend to do: Have JVP kangaroo-courts!
Perhaps, as a result of these incidents AKD’s ratings has dropped to 39%, according to the IHP survey done in April, and Sajith Premadasa’s ratings have increased gradually to match that. Whilst they are level pegging Ranil is far behind at 13%. Is this the reason why Ranil is getting his acolytes to propagate the idea that the best for the country is to extend his tenure by a referendum? He forced the postponement of Local Governments elections by refusing to release funds but he cannot do so for the presidential election for constitutional reasons. He is now looking for loopholes. Has he considered the distinct possibility that the referendum to extend the life of the presidency and the parliament if lost, would double the expenditure?
Unfortunately, this has been an exercise in futility and it would not be surprising if the next survey shows Ranil’s chances dropping even further! Perhaps, the best option available to Ranil is to retire gracefully, taking credit for steadying the economy and saving the country from an anarchic invasion of the parliament, rather than to leave politics in disgrace by coming third in the presidential election. Unless, of course, he is convinced that opinion polls do not matter and what matters is the ballots in the box!
Opinion
Thoughtfulness or mindfulness?

By Prof. Kirthi Tennakone
ktenna@yahoo.co.uk
Thoughtfulness is the quality of being conscious of issues that arise and considering action while seeking explanations. It facilitates finding solutions to problems and judging experiences.
Almost all human accomplishments are consequences of thoughtfulness.
Can you perform day-to-day work efficiently and effectively without being thoughtful? Obviously, no. Are there any major advancements attained without thought and contemplation? Not a single example!
Science and technology, art, music and literary compositions and religion stand conspicuously as products of thought.
Thought could have sinister motives and the only way to eliminate them is through thought itself. Thought could distinguish right from wrong.
Empathy, love, amusement, and expression of sorrow are reflections of thought.
Thought relieves worries by understanding or taking decisive action.
Despite the universal virtue of thoughtfulness, some advocate an idea termed mindfulness, claiming the benefits of nurturing this quality to shape mental wellbeing. The concept is defined as focusing attention to the present moment without judgment. A way of forgetting the worries and calming the mind – a form of meditation. A definition coined in the West to decouple the concept from religion. The attitude could have a temporary advantage as a method of softening negative feelings such as sorrow and anger. However, no man or woman can afford to be non-judgmental all the time. It is incompatible with indispensable thoughtfulness! What is the advantage of diverting attention to one thing without discernment during a few tens of minute’s meditation? The instructors of mindfulness meditation tell you to focus attention on trivial things. Whereas in thoughtfulness, you concentrate the mind on challenging issues. Sometimes arriving at groundbreaking scientific discoveries, solution of mathematical problems or the creation of masterpieces in engineering, art, or literature.
The concept of meditation and mindfulness originated in ancient India around 1000 BCE. Vedic ascetics believed the practice would lead to supernatural powers enabling disclosure of the truth. Failing to meet the said aspiration, notwithstanding so many stories in scripture, is discernable. Otherwise, the world would have been awakened to advancement by ancient Indians before the Greeks. The latter culture emphasized thoughtfulness!
In India, Buddha was the first to deviate from the Vedic philosophy. His teachers, Alara Kalama and Uddaka Ramaputra, were adherents of meditation. Unconvinced of their approach, Buddha concluded a thoughtful analysis of the actualities of life should be the path to realisation. However, in an environment dominated by Vedic tradition, meditation residually persisted when Buddha’s teachings transformed into a religion.
In the early 1970s, a few in the West picked up meditation and mindfulness. We Easterners, who criticize Western ideas all the time, got exalted after seeing something Eastern accepted in the Western circles. Thereafter, Easterners took up the subject more seriously, in the spirit of its definition in the West.
Today, mindfulness has become a marketable commodity – a thriving business spreading worldwide, fueled largely by advertising. There are practice centres, lessons onsite and online, and apps for purchase. Articles written by gurus of the field appear on the web.
What attracts people to mindfulness programmes? Many assume them being stressed and depressed needs to improve their mental capacity. In most instances, these are minor complaints and for understandable reasons, they do not seek mainstream medical interventions but go for exaggeratedly advertised alternatives. Mainstream medical treatments are based on rigorous science and spell out both the pros and cons of the procedure, avoiding overstatement. Whereas the alternative sector makes unsubstantiated claims about the efficacy and effectiveness of the treatment.
Advocates of mindfulness claim the benefits of their prescriptions have been proven scientifically. There are reports (mostly in open-access journals which charge a fee for publication) indicating that authors have found positive aspects of mindfulness or identified reasons correlating the efficacy of such activities. However, they rarely meet standards normally required for unequivocal acceptance. The gold standard of scientific scrutiny is the statistically significant reproducibility of claims.
If a mindfulness guru claims his prescription of meditation cures hypertension, he must record the blood pressure of participants before and after completion of the activity and show the blood pressure of a large percentage has stably dropped and repeat the experiment with different clients. He must also conduct sessions where he adopts another prescription (a placebo) under the same conditions and compares the results. This is not enough, he must request someone else to conduct sessions following his prescription, to rule out the influence of the personality of the instructor.
The laity unaware of the above rigid requirements, accede to purported claims of mindfulness proponents.
A few years ago, an article published and widely cited stated that the practice of mindfulness increases the gray matter density of the brain. A more recent study found there is no such correlation. Popular expositions on the subject do not refer to the latter report. Most mindfulness research published seems to have been conducted intending to prove the benefits of the practice. The hard science demands doing the opposite as well-experiments carried out intending to disprove the claims. You need to be skeptical until things are firmly established.
Despite many efforts diverted to disprove Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, no contradictions have been found in vain to date, strengthening the validity of the theory. Regarding mindfulness, as it stands, benefits can neither be proved nor disproved, to the gold standard of scientific scrutiny.
Some schools in foreign lands have accommodated mindfulness training programs hoping to develop the mental facility of students and Sri Lanka plans to follow. However, studies also reveal these exercises are ineffective or do more harm than good. Have we investigated this issue before imitation?
Should we force our children to focus attention on one single goal without judgment, even for a moment?
Why not allow young minds to roam wild in their deepest imagination and build castles in the air and encourage them to turn these fantasies into realities by nurturing their thoughtfulness?
Be more thoughtful than mindful?












