Foreign News
Monster iceberg ‘A23a’ just shy of a trillion tonnes
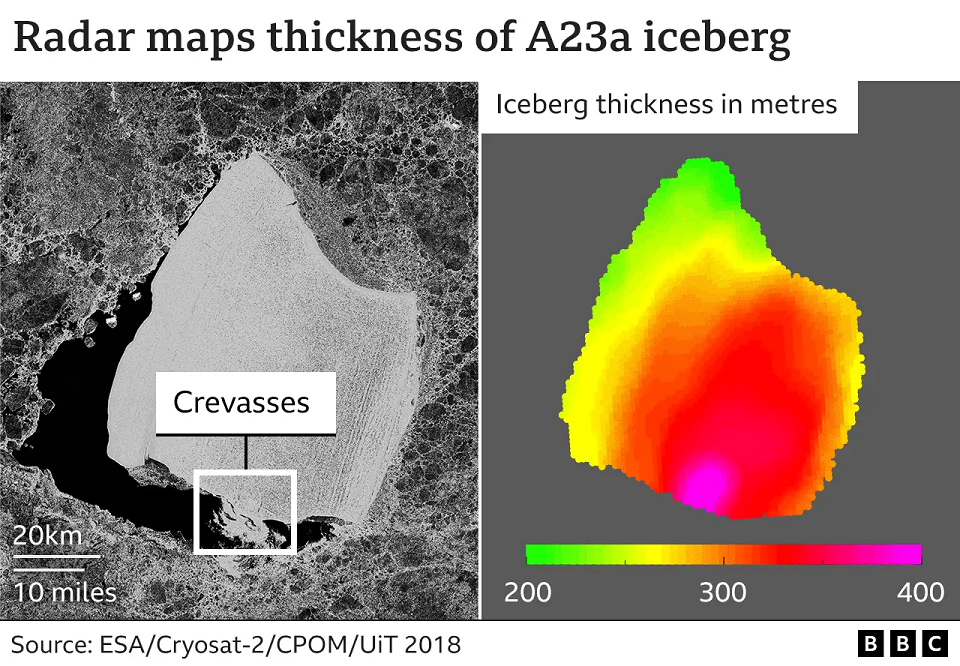
Scientists now have good numbers to describe the true scale of the world’s biggest iceberg, A23a.
Satellite measurements show the frozen block has a total average thickness of just over 280m (920ft).
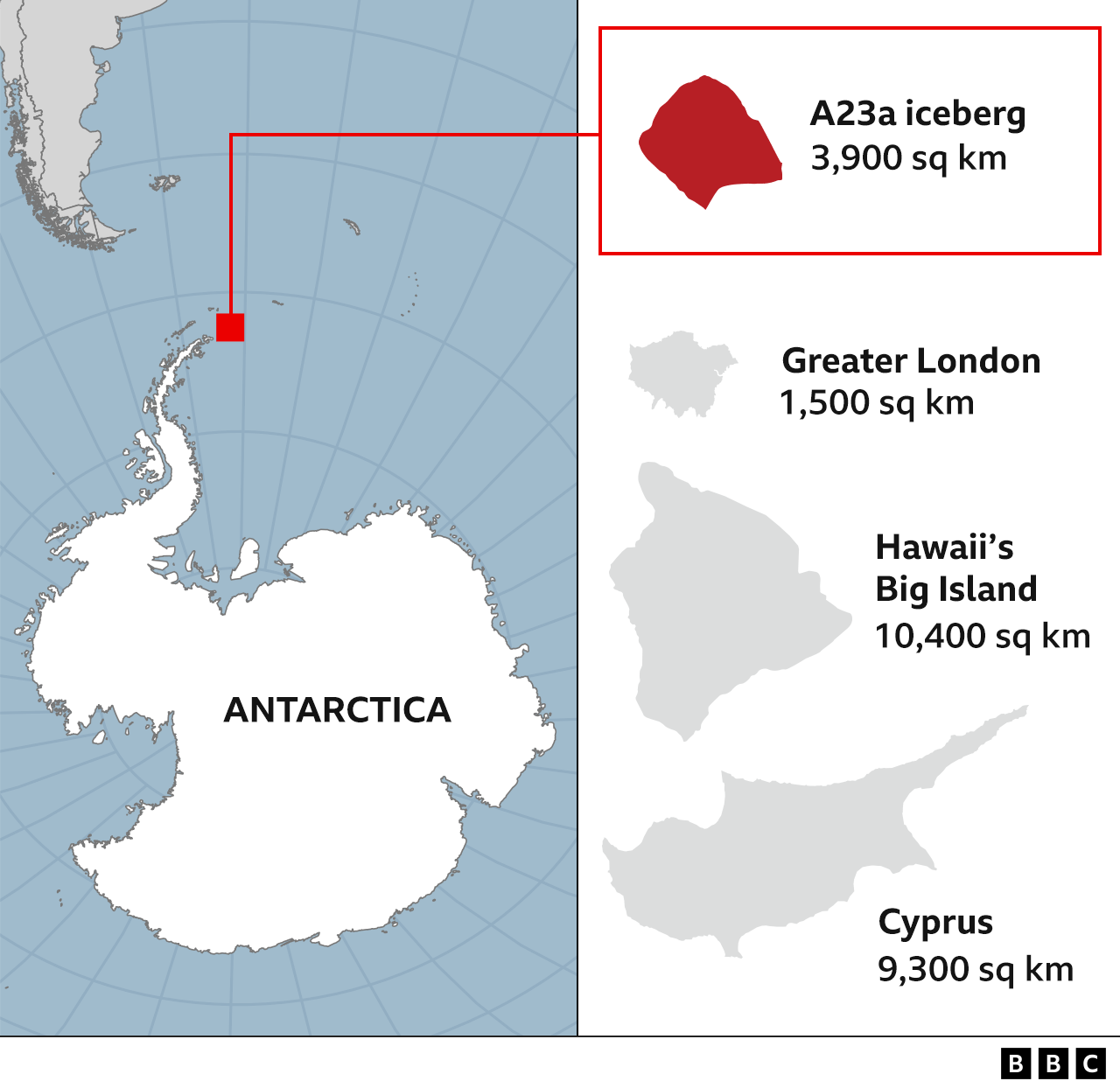
Combined with its known area of 3,900 sq km (1,500 sq miles), this gives a volume of roughly 1,100 cubic km and a mass just below a trillion tonnes.
The iceberg, which calved from the Antarctic coast in 1986, is about to drift beyond the White Continent. It has reached a critical point in its journey, researchers say, with the next few weeks likely to decide its future trajectory through the Southern Ocean.
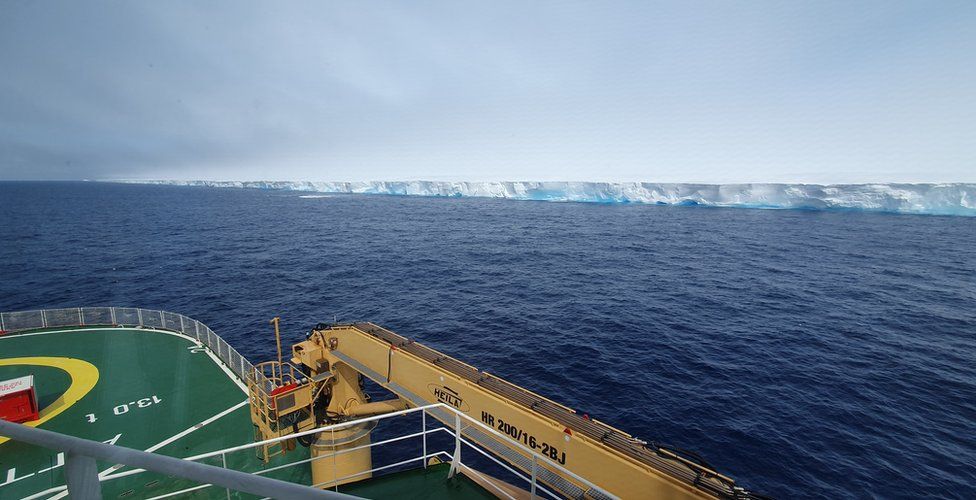

To put the new thickness data in some context, London skyscraper 22 Bishopsgate is 278m tall – bettered, in the UK, by only the 310m Shard tower.
But A23a is also more than twice the area of Greater London, giving it an overall profile much like that of a credit card.

The measurements of A23a come from the European Space Agency’s CryoSat-2 mission. This veteran spacecraft carries a radar altimeter able to sense how much of a berg’s bulk is above the waterline.
Using information about the density of ice, it is then possible to determine how much must be submerged.
“Altimetry satellites like CryoSat-2, which measure the distance to the iceberg surface and to the sea surface, allow us to monitor iceberg thickness from space,” Dr Anne Braakmann-Folgmann, from the University of Tromsø – The Arctic University of Norway, told BBC News.
“They also enable us to watch the iceberg thinning as it gets exposed to warmer ocean waters. “And together with knowledge of the sea-floor topography, we know where an iceberg will ground or when it has thinned enough to be released again.”
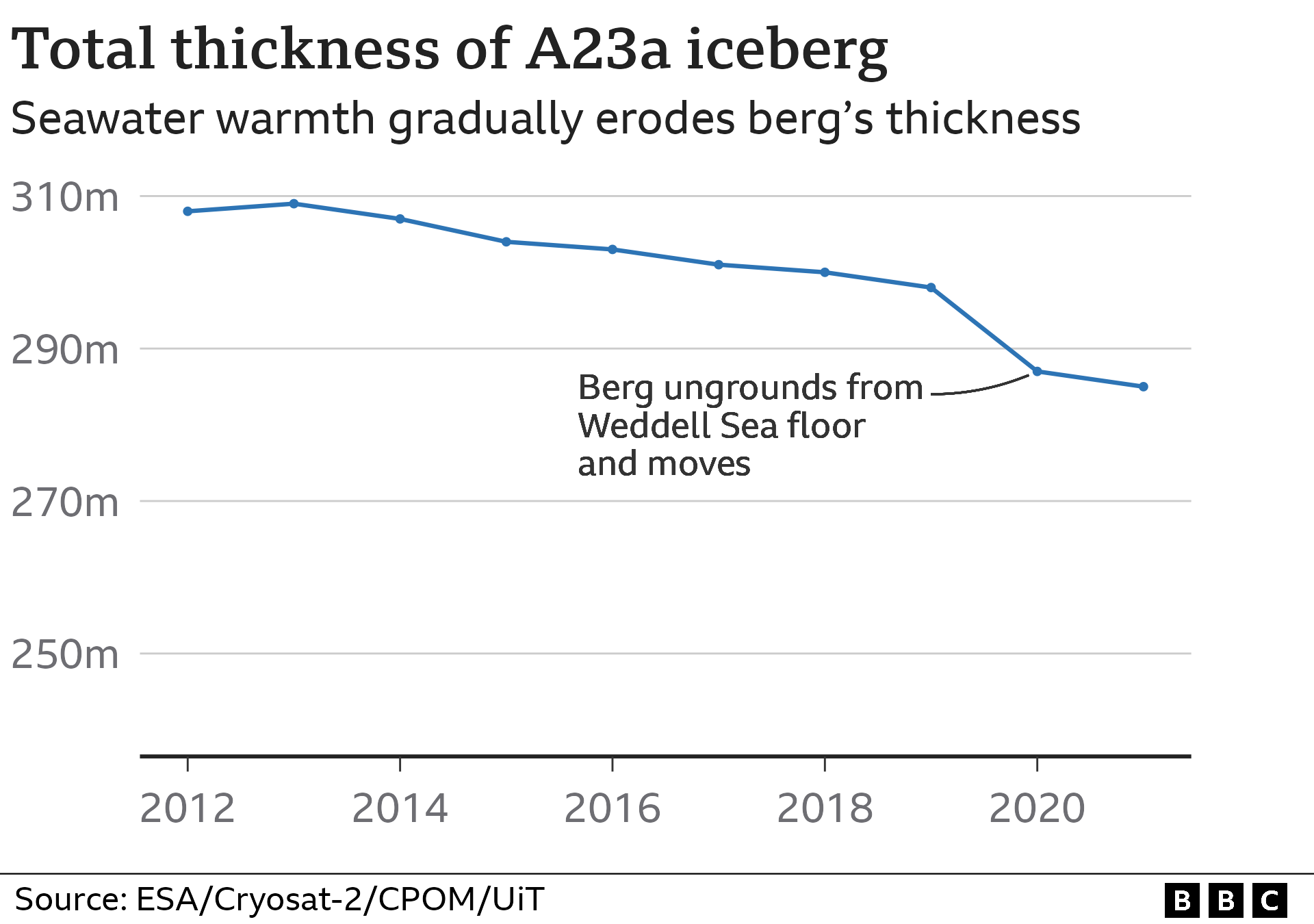
When the berg started moving, after 2020, it became increasingly difficult to obtain broad thickness measurements. But assuming an area of 3,900 sq km and an average total thickness of 285m, then A23a has a volume of 1,113 cubic km and a mass of 950 billion tonnes.

Born in a mass breakout of bergs from the Filchner Ice Shelf, in the southern Weddell Sea, A23a was almost immediately stuck in shallow bottom muds to become an “ice island” for more than three decades. And the CryoSat data can now explain why.
The berg is not a uniform block – some parts are thicker than others.
CryoSat indicates one section in particular has a very deep keel, which in 2018, had a draft – the submerged portion of an iceberg – of almost 350m and it is this section that anchored A23a for so long.
Satellite images show crevasses directly above the keel.
“This is likely the surface expression of the damage that was caused when A23a hit the seabed,” Prof Andrew Shepherd, from Northumbria University and the Natural Environment Research Council Centre for Polar Observation and Modelling (CPOM), said.
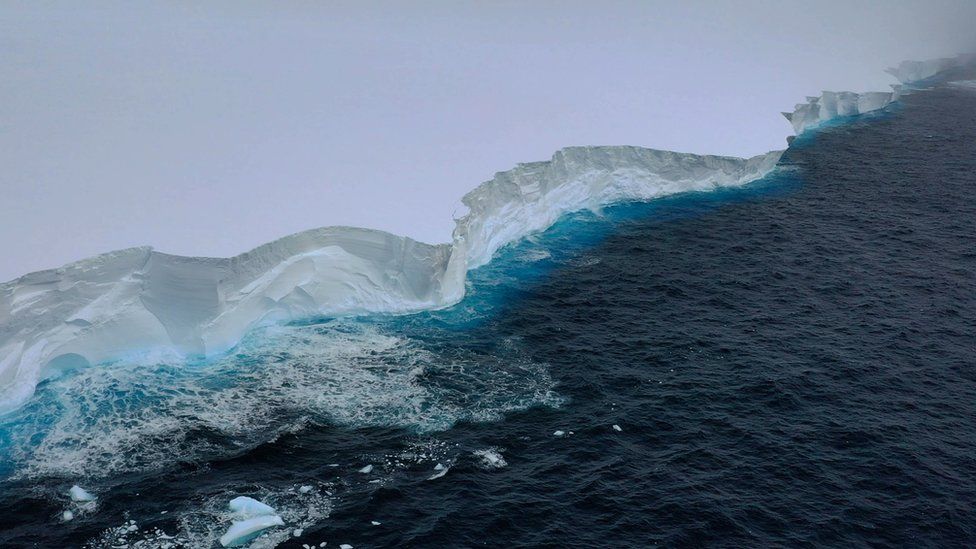

And in the years that followed, A23a gradually lost mass to eventually free itself and start moving.
“Over the last decade, we have seen a steady 2.5m per year decrease in thickness, which is what you would expect given the water temperatures in the Weddell Sea,” Dr Andy Ridout, a CPOM senior research fellow from University College London, explained.
A23a has now reached the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, where there is a convergence of various streams of fast-moving water that turn clockwise around the continent.
How it interacts with these and the westerly winds that dominate in that part of the world will control where the behemoth goes next.
But it is expected take a track called “iceberg alley” that points in the direction of the British overseas territory of South Georgia.
Scientists will follow its progress with interest.
Bergs this big have a profound influence on their environment. “They’re responsible for very deep mixing of seawater,” Prof Mike Meredith, from the British Antarctic Survey, told BBC News. “They churn ocean waters, bringing nutrients up to the surface, and, of course, they also drop a lot of dust.
“All this will fertilise the ocean – you’ll often see phytoplankton blooms in their wake.”
(BBC)
Foreign News
Nasa ‘Earthrise’ astronaut dies at 90 in plane crash

Apollo 8 astronaut Bill Anders, who snapped one of the most famous photographs taken in outer space, has died at the age of 90.
Officials say a small plane he was flying crashed into the water north of Seattle, Washington.
Anders’ son Greg confirmed that his father was flying the small plane, and that his body was recovered on Friday afternoon. “The family is devastated. He was a great pilot. He will be missed,” a statement from the family reads.
Anders – who was a lunar module pilot on the Apollo 8 mission – took the iconic Earthrise photograph, one of the most memorable and inspirational images of Earth from space.
Taken on Christmas Eve during the 1968 mission, the first crewed space flight to leave Earth and reach the Moon, the picture shows the planet rising above the horizon from the barren lunar surface.
Anders later described it as his most significant contribution to the space programme.

The image is widely credited with motivating the global environmental movement and leading to the creation of Earth Day, an annual event to promote activism and awareness of caring for the planet.
Speaking of the moment, Anders said: “We came all this way to explore the Moon, and the most important thing that we discovered was the Earth.”
Officials said on Friday that Anders crashed his plane around 11:40PDT (1940BST).
The US National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) said the 90-year-old was flying a Beechcraft A A 45 – also known as a T-34. The agency said that the plane crashed about 80ft (25m) from the coast of Jones Island.
Anders also served as the backup pilot to the Apollo 11 mission, the name of the effort that led to the first Moon landing on July 24, 1969.
Following Anders’ retirement from the space programme in 1969, the former astronaut largely worked in the aerospace industry for several decades. He also served as US Ambassador to Norway for a year in the 1970s.
But he is best remembered for the Apollo 8 mission and the iconic photograph he took from space.
“In 1968, during Apollo 8, Bill Anders offered to humanity among the deepest of gifts an astronaut can give. He traveled to the threshold of the Moon and helped all of us see something else: ourselves,” Nasa Administrator Bill Nelson said in a statement.
Mark Kelly, a former astronaut who now serves as a US Senator for the state of Arizona, said in a post on X, formerly Twitter, that Anders “inspired me and generations of astronauts and explorers. My thoughts are with his family and friends”.
[BBC]
Foreign News
China’s Chang’e-6 lifts off from far side of Moon with rock samples

A Chinese spacecraft carrying rock and soil samples from the far side of the Moon has lifted off from the lunar surface to start its journey back to Earth, according to state media.
The achievement on Tuesday is a world first and the latest leap for Beijing’s decades-old space programme, which aims to send a crewed mission to the Moon by 2030.
The Xinhua News Agency, citing the China National Space Administration (CNSA), said that the ascender of the Chang’e-6 probe took off at 7:38am local time on Tuesday (23:38 GMT) and entered a preset orbit around the moon.
It described the move as “an unprecedented feat in human lunar exploration history”.
The Chang’e-6 probe was launched last month and its lander touched down on the far side of the Moon on Sunday. It used a drill and robotic arm to dig up soil on and below the Moon’s surface, according to Xinhua.
After successfully gathering its samples, the Chang’e-6 unfurled China’s national flag for the first time on the far side of the Moon, it said.
The agency cited the CNSA as saying that the spacecraft stowed the samples it had gathered in a container inside the ascender of the probe as planned.
[Aljazeera]
Foreign News
China says its spacecraft lands on Moon’s far side

China says its uncrewed craft has successfully landed on the far side of the Moon – an unexplored place almost no-one tries to go.
The Chang’e 6 touched down in the South Pole-Aitken Basin at 06:23 Beijing time on Sunday morning (22:23 GMT Saturday), the China National Space Administration (CNSA) said.
Launched on 3 May, the mission aims to collect precious rock and soil from this region for the first time in history. The probe could extract some of the Moon’s oldest rocks from a huge crater on its South Pole.
The landing was fraught with risks, because it is very difficult to communicate with spacecraft once they reach the far side of the Moon. China is the only country to have achieved the feat before, landing its Chang’e-4 in 2019.
After launching from Wenchang Space Launch Center, the Chang’e 6 spacecraft had been orbiting the Moon waiting to land. The lander component of the mission then separated from the orbiter to touch down on the side of the Moon that faces permanently away from Earth.
During the descent, an autonomous visual obstacle avoidance system was used to automatically detect obstacles, with a visible light camera selecting a comparatively safe landing area based on the brightness and darkness of the lunar surface, the CNSA was quoted as saying by state-run Xinhua news agency.
The lander hovered about 100m (328ft) above the safe landing area, and used a laser 3D scanner before a slow vertical descent. The operation was supported by the Queqiao-2 relay satellite, the CNSA said.
Chinese state media described the successful landing as an “historic moment”. The state broadcaster said “applause erupted at the Beijing Aerospace Flight Control Center” when the Chang’e landing craft touched down on the Moon early on Sunday morning.
The lander should spend up to three days gathering materials from the surface in an operation the CNSA said would involve “many engineering innovations, high risks and great difficulty”. “Everyone is very excited that we might get a look at these rocks no-one has ever seen before,” explains Professor John Pernet-Fisher, who specialises in lunar geology at the University of Manchester.
He has analysed other lunar rock brought back on the American Apollo mission and previous Chinese missions. But he says the chance to analyse rock from a completely different area of the Moon could answer fundamental questions about how planets form.
Most of the rocks collected so far are volcanic, similar to what we might find in Iceland or Hawaii. But the material on the far side would have a different chemistry . “It would help us answer those really big questions, like how are planets formed, why do crusts form, what is the origin of water in the solar system?” the professor says.
The mission aims to collect about 2kg (4.4lb) of material using a drill and mechanical arm, according to the CNSA.
The South Pole–Aitken basin, an impact crater, is one of the largest known in the solar system.
From there, the probe could gather material that came from deep inside the lunar mantle – the inner core of the Moon – Prof Pernet-Fisher says.
The Moon’s South Pole is the next frontier in lunar missions – countries are keen to understand the region because there is a good chance it has ice.

The capsule in the last Chinese moon mission, Chang’e 5, brought back soil and rocks in 2020 (BBC)
Access to water would significantly boost the chances of successfully establishing a human base on the Moon for scientific research.
If the mission succeeds, the craft will return to Earth with the precious samples on board a special return capsule.
The material will be kept in special conditions to try to keep it as pristine as possible.
Scientists in China will be given the first chance to analyse the rocks, and later researchers around the world will be able to apply for the opportunity too.
This is the second time China has launched a mission to collect samples from the Moon.
In 2020 Chang’e 5 brought back 1.7kg of material from an area called Oceanus Procellarum on the Moon’s near side.
China is planning three more uncrewed missions this decade as it looks for water on the Moon and investigates setting up a permanent base there.
Beijing’s broader strategy aims to see a Chinese astronaut walk on the moon by around 2030.
The US also aims to put astronauts back on the moon, with Nasa aiming to launch its Artemis 3 mission in 2026.
(BBC)














