Foreign News
Key wins boost Indian PM Modi’s re-election bid
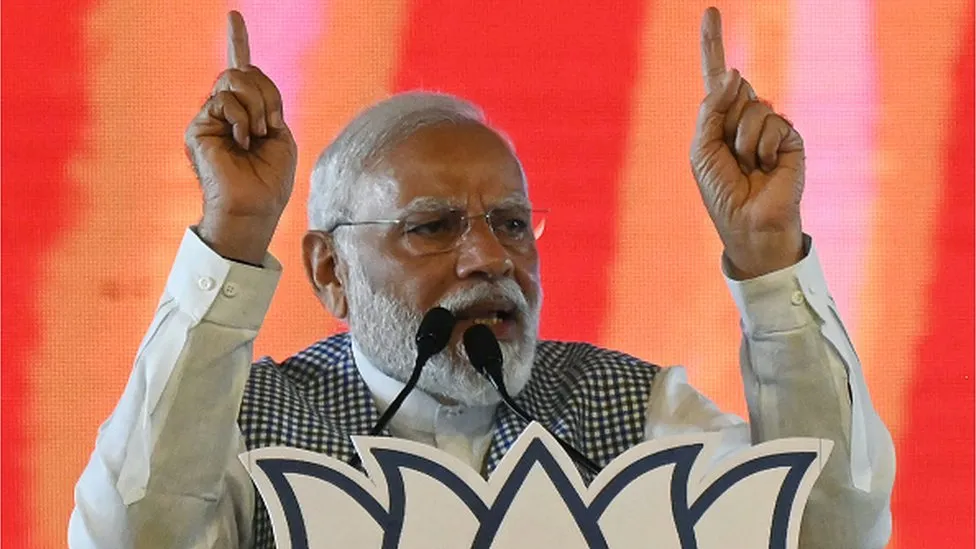

Narendra Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) is poised to win three of the four key state elections in India ahead of the crucial general elections next year.
The BJP has a commanding lead in the states of Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Chhattisgarh. The Congress is comfortably ahead in the southern state of Telangana.
More than 160 million people or a sixth of India’s electorate were eligible to vote in the polls held in November. Counting of votes for a fifth state, Mizoram, is due on Monday.
Did these elections serve a litmus test for Mr Modi’s prospects in securing a historic third term in the upcoming general elections next year? In simpler terms, would a stronger performance by the Congress have indicated a potential setback for the BJP?
Not quite. In 2018, the Congress won three key state elections – Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. Three months later BJP swept the general elections nationally and in all the three states. State elections in India are fought over state or region specific concerns, while general elections revolve around more national-level issues.
Despite this dynamic, Sunday’s results come as a significant boost for PM Modi, who is already setting his sights on a record third term next year. The win is also significant because the BJP has frequently fallen short in state elections. Until today, the party – which enjoys a comfortable majority in parliament – governed 15 of India’s 28 states – and only nine of them directly. The rest were in coalition with smaller partners.

Regaining control of Rajasthan and Chhattisgarh from the Congress and retaining Madhya Pradesh for a record fifth term means that the BJP is looking virtually unassailable in the “Hindi heartland” of northern and central India. Ten states in this Hindi-speaking belt send 225 MPs to the parliament – and BJP won 177 of the seats in 2019.
On the other hand, the elections were more important for the Congress.
An improved performance would have come as a huge morale booster and positioned the party as the natural leader of a fledgling alliance comprising 28 opposition parties, collectively known as INDIA. At one point, the party appeared to be leading in the race to win Madhya Pradesh and subsequently lost momentum as the BJP gained ground. The party has struggled to convert state victories into success in national elections in the past, and now it is failing to retain its state governments as well. Anti-incumbency is harsher on Congress.
But there is one silver lining. The Congress managed to wrest the southern state of Telangana, where the regional BRS party suffered from anti-incumbency. After a resounding win in Karnataka in May, it continues to make inroads into southern India.
So what were the factors that shaped voting behaviour in the recent polls? Beyond a track record of governance, considerations such as caste, identity, and the allure of BJP’s Hindu nationalism, welfare promises also seem to exert influence on voting patterns.

During his campaign, PM Modi announced that a scheme to provide 5kg of free grain a month to 800 million of India’s poorest people would continue for the next five years. The resurgence of his party in Madhya Pradesh was also credited to a programme offering a monthly stipend of 1,250 rupees [$16; £12] to eligible women from poorer families – women comprise some 47% of the 50 million voters in the state.
Many commentators called such welfarism by all parties competitive populism, but in reality it also underscored the vulnerable lives of millions of Indians who depend on state handouts to eke a decent living.
A nationwide poll by India Today magazine survey in August showed Mr Modi’s popularity remained intact after a decade in power: more than half of the respondents felt he should continue to lead India.
Adding to the BJP’s formidable arsenal are its massive resources, a mammoth 24/7 party organisation, governance anchored in a robust welfare architecture, and a largely supportive media. It’s hardly surprising that Mr Modi and his party appear to be in a pole position to win a stunning third term next year.
(BBC)
Foreign News
Nasa ‘Earthrise’ astronaut dies at 90 in plane crash

Apollo 8 astronaut Bill Anders, who snapped one of the most famous photographs taken in outer space, has died at the age of 90.
Officials say a small plane he was flying crashed into the water north of Seattle, Washington.
Anders’ son Greg confirmed that his father was flying the small plane, and that his body was recovered on Friday afternoon. “The family is devastated. He was a great pilot. He will be missed,” a statement from the family reads.
Anders – who was a lunar module pilot on the Apollo 8 mission – took the iconic Earthrise photograph, one of the most memorable and inspirational images of Earth from space.
Taken on Christmas Eve during the 1968 mission, the first crewed space flight to leave Earth and reach the Moon, the picture shows the planet rising above the horizon from the barren lunar surface.
Anders later described it as his most significant contribution to the space programme.

The image is widely credited with motivating the global environmental movement and leading to the creation of Earth Day, an annual event to promote activism and awareness of caring for the planet.
Speaking of the moment, Anders said: “We came all this way to explore the Moon, and the most important thing that we discovered was the Earth.”
Officials said on Friday that Anders crashed his plane around 11:40PDT (1940BST).
The US National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) said the 90-year-old was flying a Beechcraft A A 45 – also known as a T-34. The agency said that the plane crashed about 80ft (25m) from the coast of Jones Island.
Anders also served as the backup pilot to the Apollo 11 mission, the name of the effort that led to the first Moon landing on July 24, 1969.
Following Anders’ retirement from the space programme in 1969, the former astronaut largely worked in the aerospace industry for several decades. He also served as US Ambassador to Norway for a year in the 1970s.
But he is best remembered for the Apollo 8 mission and the iconic photograph he took from space.
“In 1968, during Apollo 8, Bill Anders offered to humanity among the deepest of gifts an astronaut can give. He traveled to the threshold of the Moon and helped all of us see something else: ourselves,” Nasa Administrator Bill Nelson said in a statement.
Mark Kelly, a former astronaut who now serves as a US Senator for the state of Arizona, said in a post on X, formerly Twitter, that Anders “inspired me and generations of astronauts and explorers. My thoughts are with his family and friends”.
[BBC]
Foreign News
China’s Chang’e-6 lifts off from far side of Moon with rock samples

A Chinese spacecraft carrying rock and soil samples from the far side of the Moon has lifted off from the lunar surface to start its journey back to Earth, according to state media.
The achievement on Tuesday is a world first and the latest leap for Beijing’s decades-old space programme, which aims to send a crewed mission to the Moon by 2030.
The Xinhua News Agency, citing the China National Space Administration (CNSA), said that the ascender of the Chang’e-6 probe took off at 7:38am local time on Tuesday (23:38 GMT) and entered a preset orbit around the moon.
It described the move as “an unprecedented feat in human lunar exploration history”.
The Chang’e-6 probe was launched last month and its lander touched down on the far side of the Moon on Sunday. It used a drill and robotic arm to dig up soil on and below the Moon’s surface, according to Xinhua.
After successfully gathering its samples, the Chang’e-6 unfurled China’s national flag for the first time on the far side of the Moon, it said.
The agency cited the CNSA as saying that the spacecraft stowed the samples it had gathered in a container inside the ascender of the probe as planned.
[Aljazeera]
Foreign News
China says its spacecraft lands on Moon’s far side

China says its uncrewed craft has successfully landed on the far side of the Moon – an unexplored place almost no-one tries to go.
The Chang’e 6 touched down in the South Pole-Aitken Basin at 06:23 Beijing time on Sunday morning (22:23 GMT Saturday), the China National Space Administration (CNSA) said.
Launched on 3 May, the mission aims to collect precious rock and soil from this region for the first time in history. The probe could extract some of the Moon’s oldest rocks from a huge crater on its South Pole.
The landing was fraught with risks, because it is very difficult to communicate with spacecraft once they reach the far side of the Moon. China is the only country to have achieved the feat before, landing its Chang’e-4 in 2019.
After launching from Wenchang Space Launch Center, the Chang’e 6 spacecraft had been orbiting the Moon waiting to land. The lander component of the mission then separated from the orbiter to touch down on the side of the Moon that faces permanently away from Earth.
During the descent, an autonomous visual obstacle avoidance system was used to automatically detect obstacles, with a visible light camera selecting a comparatively safe landing area based on the brightness and darkness of the lunar surface, the CNSA was quoted as saying by state-run Xinhua news agency.
The lander hovered about 100m (328ft) above the safe landing area, and used a laser 3D scanner before a slow vertical descent. The operation was supported by the Queqiao-2 relay satellite, the CNSA said.
Chinese state media described the successful landing as an “historic moment”. The state broadcaster said “applause erupted at the Beijing Aerospace Flight Control Center” when the Chang’e landing craft touched down on the Moon early on Sunday morning.
The lander should spend up to three days gathering materials from the surface in an operation the CNSA said would involve “many engineering innovations, high risks and great difficulty”. “Everyone is very excited that we might get a look at these rocks no-one has ever seen before,” explains Professor John Pernet-Fisher, who specialises in lunar geology at the University of Manchester.
He has analysed other lunar rock brought back on the American Apollo mission and previous Chinese missions. But he says the chance to analyse rock from a completely different area of the Moon could answer fundamental questions about how planets form.
Most of the rocks collected so far are volcanic, similar to what we might find in Iceland or Hawaii. But the material on the far side would have a different chemistry . “It would help us answer those really big questions, like how are planets formed, why do crusts form, what is the origin of water in the solar system?” the professor says.
The mission aims to collect about 2kg (4.4lb) of material using a drill and mechanical arm, according to the CNSA.
The South Pole–Aitken basin, an impact crater, is one of the largest known in the solar system.
From there, the probe could gather material that came from deep inside the lunar mantle – the inner core of the Moon – Prof Pernet-Fisher says.
The Moon’s South Pole is the next frontier in lunar missions – countries are keen to understand the region because there is a good chance it has ice.

The capsule in the last Chinese moon mission, Chang’e 5, brought back soil and rocks in 2020 (BBC)
Access to water would significantly boost the chances of successfully establishing a human base on the Moon for scientific research.
If the mission succeeds, the craft will return to Earth with the precious samples on board a special return capsule.
The material will be kept in special conditions to try to keep it as pristine as possible.
Scientists in China will be given the first chance to analyse the rocks, and later researchers around the world will be able to apply for the opportunity too.
This is the second time China has launched a mission to collect samples from the Moon.
In 2020 Chang’e 5 brought back 1.7kg of material from an area called Oceanus Procellarum on the Moon’s near side.
China is planning three more uncrewed missions this decade as it looks for water on the Moon and investigates setting up a permanent base there.
Beijing’s broader strategy aims to see a Chinese astronaut walk on the moon by around 2030.
The US also aims to put astronauts back on the moon, with Nasa aiming to launch its Artemis 3 mission in 2026.
(BBC)