Foreign News
Kenneth Eugene Smith faces first nitrogen execution in US after losing last-minute appeals
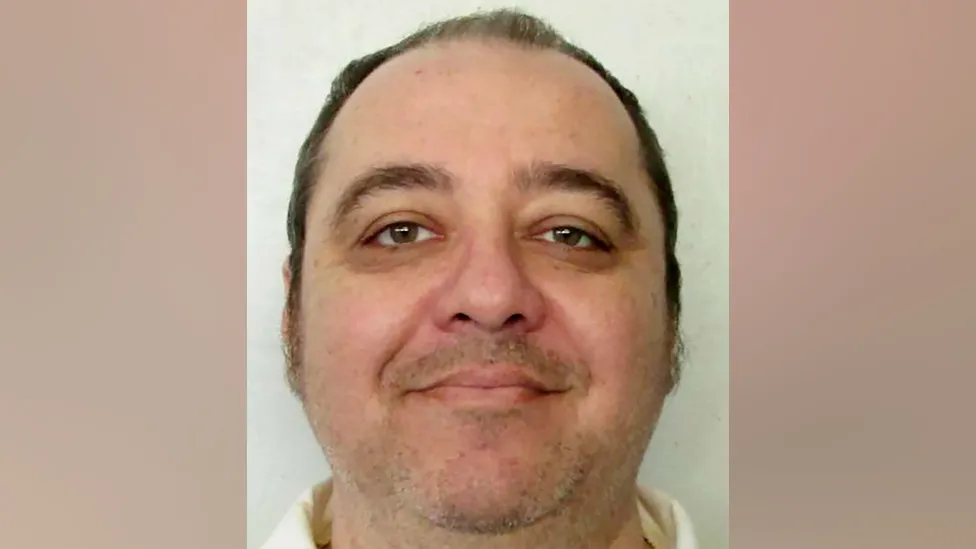

An Alabama death row inmate is expected to become the first person in the US to be executed with nitrogen gas, after losing last-minute appeals.
The US Supreme Court and a lower appeals court declined to block what Kenneth Eugene Smith’s lawyers called a “cruel and unusual” punishment.
Opponents say using nitrogen could cause unnecessary suffering, and a leak could harm people present in the room.
Smith, 58, was convicted in 1989 of murdering Elizabeth Sennett.
Alabama has 30 hours to carry out the execution, which involves pumping nitrogen gas through a mask, from Thursday at 0600 GMT (0100 ET).
He told the BBC earlier this week that the wait felt like torture.
Smith would be the first person to be put to death by this method in the US and, according to the Death Penalty Information Center, anywhere in the world.
Lawyers for the inmate, who has been on death row since 1996, told the BBC on Wednesday night that they were lodging another appeal to the nation’s top court in the hope of a last minute reprieve.
Breathing pure nitrogen without oxygen causes the cells to break down and leads to death. Alabama said in a court filing that they expect him to lose consciousness within seconds and die in a matter of minutes. But its use has been denounced by some medical professionals, who warn it could cause a range of catastrophic mishaps, ranging from violent convulsions to survival in a vegetative state.
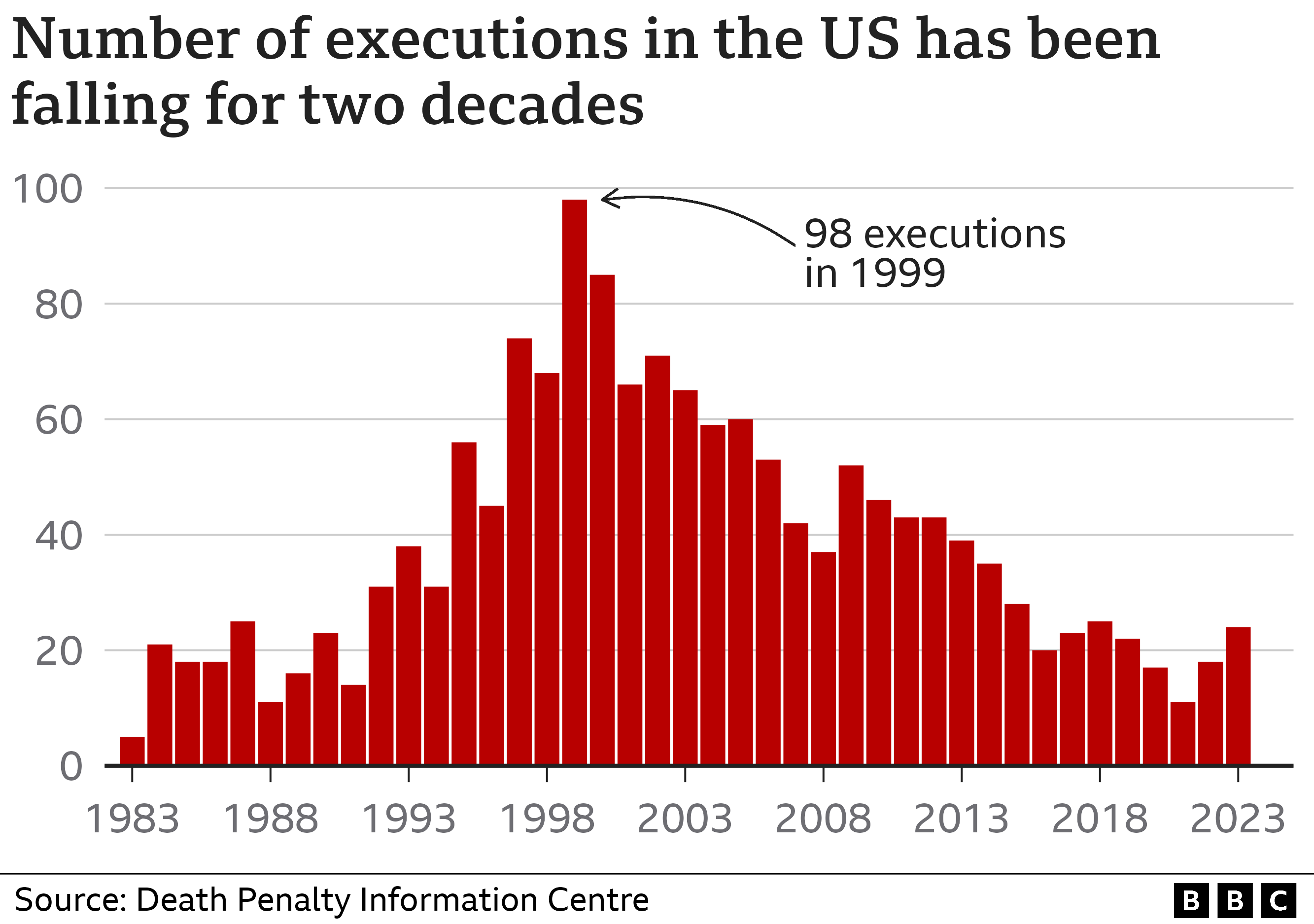
Alabama and two other US states have approved the use of nitrogen hypoxia as an alternative method of execution because the drugs used in lethal injections have become more difficult to find, contributing to a fall in the number of executions nationally.
Alabama already tried to execute Smith by lethal injection two years ago but were unable to raise a vein before the state’s death warrant expired.
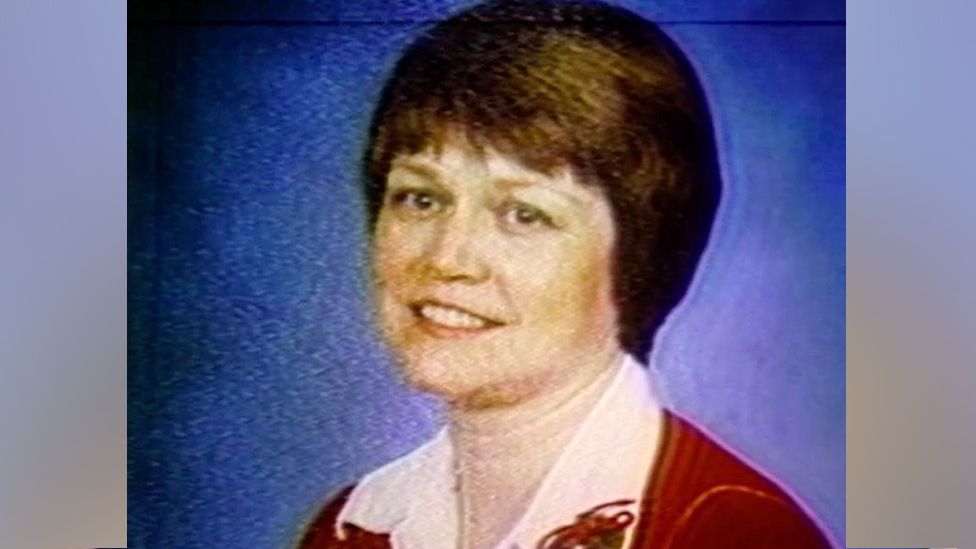

Smith was one of two men convicted of murdering 45-year-old Sennett in a $1,000 (£790) killing-for-hire in March 1988. She was beaten with a fireplace implement and stabbed in the chest and neck, and her death was staged to look like a home invasion and burglary.
Her husband Charles Sennett, a debt-ridden preacher, had orchestrated the scheme to collect insurance money. He killed himself as investigators closed in. Smith’s fellow hitman, John Forrest Parker, was executed in 2010.
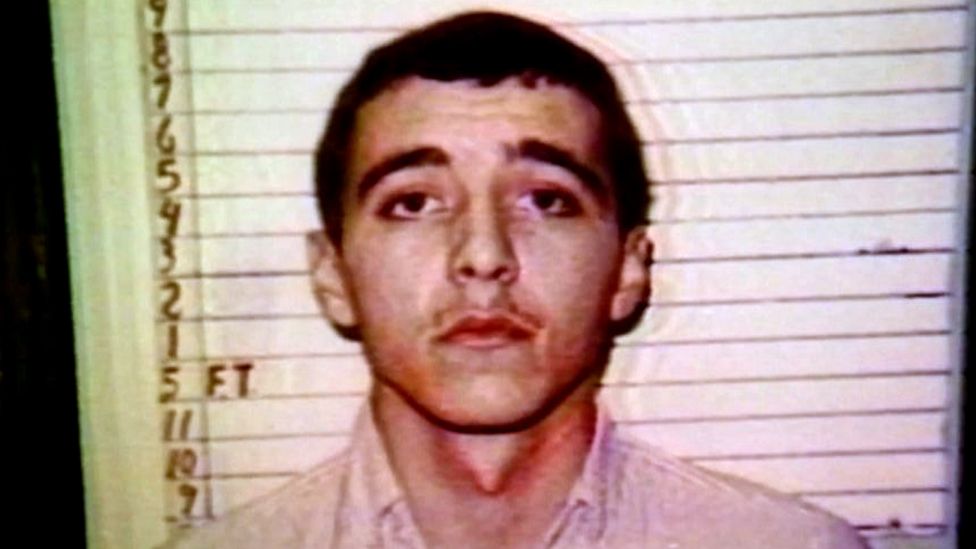

At his trial Smith admitted to being present when the victim was killed, but said he did not take part in the attack.
The UN’s High Commissioner for Human Rights has said gassing Smith could amount to torture or other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment, and called for a halt. Smith’s lawyers lodged a challenge with the Supreme Court, arguing that putting convicts through multiple execution attempts violates the Eighth Amendment of the US Constitution, which protects against “cruel and unusual” punishment.
On Wednesday, the justices declined to hear the appeal and denied his request to halt the execution. No justice publicly dissented from the ruling.
Smith also made a separate legal challenge to the lower 11th US Circuit Court of Appeals, where he contested the legality of Alabama’s nitrogen gas protocol. But that court also rejected the inmate’s request for an injunction in a ruling on Wednesday evening.
Smith’s lawyers said they would again appeal to the Supreme Court.
His legal team argue the nitrogen gas method is “recently released and untested”, leaving him at risk of choking on his own vomit.
State Attorney General Steve Marshall previously called it “perhaps the most humane method of execution ever devised”.
Smith’s spiritual adviser, Reverend Jeff Hood, will be present in the room when the execution happens. He told the BBC he believes he will be in danger if the nitrogen leaks.
On Wednesday, prison officials escorted Rev Hood for a “walk-through” of the execution chamber, as required by Alabama’s execution protocol.
He told the BBC afterwards that he saw oxygen-level meters unplugged on a ledge inside the room, which he described as “unbelievably disturbing, it feels like you are at the centre of evil”.
“I asked ‘what’s the safety plan?’ and they said they didn’t want to get into it, they couldn’t get into it,” he said. “Once again we’re back at this place of having to rely on these people who have botched three executions in the last few years, he said. “It’s absolutely a terrifying thing to think that your life hangs in the balance with these guys”.
Rev Hood said he had requested that Alabama’s Governor Kay Ivey be present in the chamber during the execution to demonstrate her confidence in its safety, but had not received a response. “We have somebody who is championing this type of execution in the governor and yet she is unwilling to get her hands dirty,” he said.
The BBC has approached Ms Ivey’s office for comment regarding this and the latest accusations over safety.
Alabama has one of the highest per capita execution rates in the US and has 165 people currently on death row.
Since 2018, the state has been responsible for three botched attempts at lethal injection in which the condemned inmates survived.
The failures led to an internal review that largely placed blame on the prisoners themselves.
(BBC)
Foreign News
Nasa ‘Earthrise’ astronaut dies at 90 in plane crash

Apollo 8 astronaut Bill Anders, who snapped one of the most famous photographs taken in outer space, has died at the age of 90.
Officials say a small plane he was flying crashed into the water north of Seattle, Washington.
Anders’ son Greg confirmed that his father was flying the small plane, and that his body was recovered on Friday afternoon. “The family is devastated. He was a great pilot. He will be missed,” a statement from the family reads.
Anders – who was a lunar module pilot on the Apollo 8 mission – took the iconic Earthrise photograph, one of the most memorable and inspirational images of Earth from space.
Taken on Christmas Eve during the 1968 mission, the first crewed space flight to leave Earth and reach the Moon, the picture shows the planet rising above the horizon from the barren lunar surface.
Anders later described it as his most significant contribution to the space programme.

The image is widely credited with motivating the global environmental movement and leading to the creation of Earth Day, an annual event to promote activism and awareness of caring for the planet.
Speaking of the moment, Anders said: “We came all this way to explore the Moon, and the most important thing that we discovered was the Earth.”
Officials said on Friday that Anders crashed his plane around 11:40PDT (1940BST).
The US National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) said the 90-year-old was flying a Beechcraft A A 45 – also known as a T-34. The agency said that the plane crashed about 80ft (25m) from the coast of Jones Island.
Anders also served as the backup pilot to the Apollo 11 mission, the name of the effort that led to the first Moon landing on July 24, 1969.
Following Anders’ retirement from the space programme in 1969, the former astronaut largely worked in the aerospace industry for several decades. He also served as US Ambassador to Norway for a year in the 1970s.
But he is best remembered for the Apollo 8 mission and the iconic photograph he took from space.
“In 1968, during Apollo 8, Bill Anders offered to humanity among the deepest of gifts an astronaut can give. He traveled to the threshold of the Moon and helped all of us see something else: ourselves,” Nasa Administrator Bill Nelson said in a statement.
Mark Kelly, a former astronaut who now serves as a US Senator for the state of Arizona, said in a post on X, formerly Twitter, that Anders “inspired me and generations of astronauts and explorers. My thoughts are with his family and friends”.
[BBC]
Foreign News
China’s Chang’e-6 lifts off from far side of Moon with rock samples

A Chinese spacecraft carrying rock and soil samples from the far side of the Moon has lifted off from the lunar surface to start its journey back to Earth, according to state media.
The achievement on Tuesday is a world first and the latest leap for Beijing’s decades-old space programme, which aims to send a crewed mission to the Moon by 2030.
The Xinhua News Agency, citing the China National Space Administration (CNSA), said that the ascender of the Chang’e-6 probe took off at 7:38am local time on Tuesday (23:38 GMT) and entered a preset orbit around the moon.
It described the move as “an unprecedented feat in human lunar exploration history”.
The Chang’e-6 probe was launched last month and its lander touched down on the far side of the Moon on Sunday. It used a drill and robotic arm to dig up soil on and below the Moon’s surface, according to Xinhua.
After successfully gathering its samples, the Chang’e-6 unfurled China’s national flag for the first time on the far side of the Moon, it said.
The agency cited the CNSA as saying that the spacecraft stowed the samples it had gathered in a container inside the ascender of the probe as planned.
[Aljazeera]
Foreign News
China says its spacecraft lands on Moon’s far side

China says its uncrewed craft has successfully landed on the far side of the Moon – an unexplored place almost no-one tries to go.
The Chang’e 6 touched down in the South Pole-Aitken Basin at 06:23 Beijing time on Sunday morning (22:23 GMT Saturday), the China National Space Administration (CNSA) said.
Launched on 3 May, the mission aims to collect precious rock and soil from this region for the first time in history. The probe could extract some of the Moon’s oldest rocks from a huge crater on its South Pole.
The landing was fraught with risks, because it is very difficult to communicate with spacecraft once they reach the far side of the Moon. China is the only country to have achieved the feat before, landing its Chang’e-4 in 2019.
After launching from Wenchang Space Launch Center, the Chang’e 6 spacecraft had been orbiting the Moon waiting to land. The lander component of the mission then separated from the orbiter to touch down on the side of the Moon that faces permanently away from Earth.
During the descent, an autonomous visual obstacle avoidance system was used to automatically detect obstacles, with a visible light camera selecting a comparatively safe landing area based on the brightness and darkness of the lunar surface, the CNSA was quoted as saying by state-run Xinhua news agency.
The lander hovered about 100m (328ft) above the safe landing area, and used a laser 3D scanner before a slow vertical descent. The operation was supported by the Queqiao-2 relay satellite, the CNSA said.
Chinese state media described the successful landing as an “historic moment”. The state broadcaster said “applause erupted at the Beijing Aerospace Flight Control Center” when the Chang’e landing craft touched down on the Moon early on Sunday morning.
The lander should spend up to three days gathering materials from the surface in an operation the CNSA said would involve “many engineering innovations, high risks and great difficulty”. “Everyone is very excited that we might get a look at these rocks no-one has ever seen before,” explains Professor John Pernet-Fisher, who specialises in lunar geology at the University of Manchester.
He has analysed other lunar rock brought back on the American Apollo mission and previous Chinese missions. But he says the chance to analyse rock from a completely different area of the Moon could answer fundamental questions about how planets form.
Most of the rocks collected so far are volcanic, similar to what we might find in Iceland or Hawaii. But the material on the far side would have a different chemistry . “It would help us answer those really big questions, like how are planets formed, why do crusts form, what is the origin of water in the solar system?” the professor says.
The mission aims to collect about 2kg (4.4lb) of material using a drill and mechanical arm, according to the CNSA.
The South Pole–Aitken basin, an impact crater, is one of the largest known in the solar system.
From there, the probe could gather material that came from deep inside the lunar mantle – the inner core of the Moon – Prof Pernet-Fisher says.
The Moon’s South Pole is the next frontier in lunar missions – countries are keen to understand the region because there is a good chance it has ice.

The capsule in the last Chinese moon mission, Chang’e 5, brought back soil and rocks in 2020 (BBC)
Access to water would significantly boost the chances of successfully establishing a human base on the Moon for scientific research.
If the mission succeeds, the craft will return to Earth with the precious samples on board a special return capsule.
The material will be kept in special conditions to try to keep it as pristine as possible.
Scientists in China will be given the first chance to analyse the rocks, and later researchers around the world will be able to apply for the opportunity too.
This is the second time China has launched a mission to collect samples from the Moon.
In 2020 Chang’e 5 brought back 1.7kg of material from an area called Oceanus Procellarum on the Moon’s near side.
China is planning three more uncrewed missions this decade as it looks for water on the Moon and investigates setting up a permanent base there.
Beijing’s broader strategy aims to see a Chinese astronaut walk on the moon by around 2030.
The US also aims to put astronauts back on the moon, with Nasa aiming to launch its Artemis 3 mission in 2026.
(BBC)