Features
Comparing external debt burdens: Sri Lanka and middle-income countries

 Middle-income countries (MICs), comprising 106 diverse nations, face challenges comparable to low-income countries, including high debt and economic competitiveness issues. Despite their potential economic strength, they risk stagnation, particularly post-COVID-19. These concerns are echoed by numerous global organisations and institutions, as outlined below.
Middle-income countries (MICs), comprising 106 diverse nations, face challenges comparable to low-income countries, including high debt and economic competitiveness issues. Despite their potential economic strength, they risk stagnation, particularly post-COVID-19. These concerns are echoed by numerous global organisations and institutions, as outlined below.
UN General Assembly President Volkan Bozkir emphasises the urgency to address structural obstacles hindering Sustainable Development Goal achievement in MICs. Crippling debt is a major challenge exacerbated by the pandemic, with MICs facing a higher debt service ratio than low-income countries.
The UNCTAD emphasises the need for comprehensive debt relief and restructuring involving all creditors to ensure a sustainable and equitable recovery. Exclusion from debt relief initiatives poses a threat to global poverty, inequality, and climate change efforts if the international community fails to support MICs.
Then Ajay Banga, who assumed the role of World Bank Group President on June 2, 2023, has highlighted the multifaceted role of the World Bank, emphasising its financial support and the importance of knowledge and expertise. His claim of providing over US$ 100 billion to the poorest countries and Middle-Income Countries (MICs) indicates a substantial financial commitment by the World Bank.
However, a critical perspective would question the effectiveness of these funds and their impact on addressing the stated issues. It is crucial to assess the outcomes and benefits derived from the financial assistance as some of these countries, including Sri Lanka, have not utilised their borrowed funds in economically viable and financially feasible projects. The emphasis on the World Bank as a “knowledge bank” raises questions about how effectively this expertise is shared and utilized by recipient countries. The practical application and impact of knowledge-sharing need to be scrutinised.
The World Bank’s classification of Middle-Income Countries, based on Gross National Income (GNI) per capita, may be seen as a straightforward economic metric. MICs include countries with Gross National Income (GNI) between US$1,86 and US$13,205 comprising both lower middle-income countries and upper middle-income countries. Together, MICs account for about 30 percent of global GDP and make up 75 percent of the world’s population, including 60 percent of the world’s poor.
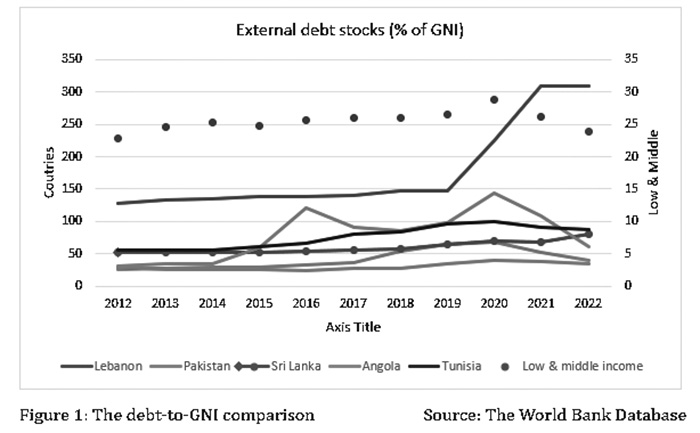
The debt-to-GNI comparison for Argentina, Angola, Pakistan, Sri Lanka and Tunisia, in relation to low and middle-income countries, can be illustrated as per Figure 1, which shows the external debt stocks as a percentage of Gross National Income (GNI) for the years 2012 to 2022 for low and middle-income countries, along with specific data for Angola, Lebanon, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Tunisia.
The number for low and middle-income countries has been gradually increasing over the years, from approximately 22.8% in 2012 to around 24.2% in 2022. Lebanon stands out with an exceptionally high external debt-to-GNI ratio, reaching 309.2% in 2021. Pakistan’s number has shown fluctuations but has generally increased, going from 28.9% in 2012 to 38.1% in 2022. Sri Lanka has experienced a steady increase in external debt, growing from 51.6% in 2012 to 88.9% in 2022. Angola’s external debt has shown a substantial increase over the years, more than tripling from 31.5% in 2012 to 109.5% in 2021 but with a sharp drop to 60.8% in 2022.
Sri Lanka has shown a consistent upward trend in external debt as a percentage of GNI from 2012 to 2022. In 2022, Sri Lanka’s external debt as a percentage of GNI (67.9%) is higher than Argentina (51.6%), Pakistan (38.1%) and Angola (60.8%) but just below Tunisia (87.6%) and well below Lebanon (>300%). Despite Sri Lanka being positioned in the mid-range among the selected countries, it exhibits a lack of progress in contrast to other nations that have demonstrated some recovery in 2022, compared to 2020 and 2021.
As we all witnessed, Sri Lanka’s rising debt levels may pose challenges in terms of debt sustainability and economic stability. It could impact the country’s ability to meet its financial obligations and fund development initiatives.

In Figure 2 (Debt per head), it is noteworthy that there are no intersecting lines, indicating a consistent pattern over the 10-year period. This implies that these five countries maintained comparable positions in terms of external debt per capita throughout the decade, showcasing a consistent alignment in their relative debt levels.
While all the countries experienced increases in debt over the period, Argentina’s debt per capita remained higher than Sri Lanka’s. Lebanon had significantly higher external debt per capita compared to Sri Lanka. Despite increases in debt for both countries, Lebanon’s debt per capita remained much higher than Sri Lanka’s. Sri Lanka had a higher external debt per capita. Both countries experienced increases in debt, with Sri Lanka consistently having a higher debt per capita than Pakistan.
Secretary-General of the United Nations, António Guterres, has called for the reform of international financial and development institutions to better represent the interests of the Global South. He has emphasised the need for these institutions, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, to evolve to match today’s global economy. Guterres highlighted the importance of ensuring that these institutions are truly universal and inclusive, reflecting the realities of the current global economic landscape.
Reflecting on the geopolitical landscape, Guterres remarked on the shift away from a bipolar or unipolar world to a more chaotic, multipolar one. He highlighted the need for constructive dialogue between developed and developing nations to address conflicts, climate change, and other pressing issues.
UN Deputy Secretary-General Amina Mohammed emphasised the crucial role of MICs in global growth, constituting close to one-third of the world’s GDP and serving as major drivers of sustainable development. Despite their economic significance, vulnerabilities persist in MICs, with 62 percent of the world’s poor residing in these countries. She also pointed out that 39 MICs now face net interest payments exceeding 10 percent of government revenue, a significant increase from 23 countries a decade ago. This situation underscores the complex and multifaceted challenges that MICs encounter, necessitating global attention and support to ensure sustained economic recovery and resilience.
On a different track, Anuradha Mittal, Executive Director of the Oakland Institute, has highlighted the impact of right-wing politics on MICs like Brazil. She emphasises that the challenges faced by MICs are similar to wealthier nations and depend on the election of officials committed to the public good. Mittal underscores the global challenge for MICs in navigating political allegiances amid conflicts like those in Ukraine and the Middle East, hindering the necessary global cooperation for social and environmental progress, especially in addressing the climate emergency.
Bhumika Muchhala, a political economist with Third World Network, criticises the lack of acknowledgement of rich countries, especially the US, for their international responsibility in causing cross-border spillovers that violate the economic and social rights of other nations.
In conclusion, this comprehensive analysis delves into the multifaceted dynamics surrounding Middle-Income Countries (MICs) and their role in the global arena. The Group of 77 acts as a pivotal force in uniting developing nations, but concerns arise regarding its ability to address the diverse needs of its 134-member nations effectively. MICs, encompassing 106 nations, face challenges akin to low-income countries, including high debt and economic competitiveness issues, posing risks of stagnation post-COVID-19. The UN emphasises the urgency to fine-tune the development system to meet the unique needs of MICs, with a focus on addressing crippling debt exacerbated by the pandemic.
World Bank President Ajay Banga’s statements underscore the institution’s financial commitment and knowledge-sharing approach. However, critical scrutiny is warranted to assess the tangible impact of funds and the effectiveness of knowledge dissemination. The external debt comparison for Angola, Argentina, Lebanon, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Tunisia with that of aggregate MICs reveals varying degrees of vulnerability, with Lebanon facing exceptionally high levels. Sri Lanka’s mid-range position signals the importance of monitoring rising debt levels for sustainable economic development.
Additionally, insights from Anuradha Mittal shed light on the impact of right-wing politics on MICs, citing Brazil as a case study. The challenges faced by MICs are intertwined with political landscapes, influencing social and environmental policies. Bhumika Muchhala critically examines the adverse spillovers of the Federal Reserve’s monetary tightening, exacerbating sovereign debt distress and creating a crisis of inequality. The international community’s responsibility for addressing cross-border spillovers is underscored, urging support for MICs to prevent threats to global poverty, inequality, and climate change efforts. This analysis calls for collaborative efforts to navigate challenges and leverage opportunities for MICs on the global stage.
(The writer, a senior Chartered Accountant and professional banker, is Professor at SLIIT University, Malabe. He is also the author of the “Doing Social Research and Publishing Results”, a Springer publication (Singapore), and “Samaja Gaveshakaya (in Sinhala). The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the institution he works for. He can be contacted at saliya.a@slit.lk and www.researcher.com)
Features
The heart-friendly health minister

by Dr Gotabhya Ranasinghe
Senior Consultant Cardiologist
National Hospital Sri Lanka
When we sought a meeting with Hon Dr. Ramesh Pathirana, Minister of Health, he graciously cleared his busy schedule to accommodate us. Renowned for his attentive listening and deep understanding, Minister Pathirana is dedicated to advancing the health sector. His openness and transparency exemplify the qualities of an exemplary politician and minister.
Dr. Palitha Mahipala, the current Health Secretary, demonstrates both commendable enthusiasm and unwavering support. This combination of attributes makes him a highly compatible colleague for the esteemed Minister of Health.
Our discussion centered on a project that has been in the works for the past 30 years, one that no other minister had managed to advance.
Minister Pathirana, however, recognized the project’s significance and its potential to revolutionize care for heart patients.
The project involves the construction of a state-of-the-art facility at the premises of the National Hospital Colombo. The project’s location within the premises of the National Hospital underscores its importance and relevance to the healthcare infrastructure of the nation.
This facility will include a cardiology building and a tertiary care center, equipped with the latest technology to handle and treat all types of heart-related conditions and surgeries.
Securing funding was a major milestone for this initiative. Minister Pathirana successfully obtained approval for a $40 billion loan from the Asian Development Bank. With the funding in place, the foundation stone is scheduled to be laid in September this year, and construction will begin in January 2025.
This project guarantees a consistent and uninterrupted supply of stents and related medications for heart patients. As a result, patients will have timely access to essential medical supplies during their treatment and recovery. By securing these critical resources, the project aims to enhance patient outcomes, minimize treatment delays, and maintain the highest standards of cardiac care.
Upon its fruition, this monumental building will serve as a beacon of hope and healing, symbolizing the unwavering dedication to improving patient outcomes and fostering a healthier society.We anticipate a future marked by significant progress and positive outcomes in Sri Lanka’s cardiovascular treatment landscape within the foreseeable timeframe.
Features
A LOVING TRIBUTE TO JESUIT FR. ALOYSIUS PIERIS ON HIS 90th BIRTHDAY

by Fr. Emmanuel Fernando, OMI
Jesuit Fr. Aloysius Pieris (affectionately called Fr. Aloy) celebrated his 90th birthday on April 9, 2024 and I, as the editor of our Oblate Journal, THE MISSIONARY OBLATE had gone to press by that time. Immediately I decided to publish an article, appreciating the untiring selfless services he continues to offer for inter-Faith dialogue, the renewal of the Catholic Church, his concern for the poor and the suffering Sri Lankan masses and to me, the present writer.
It was in 1988, when I was appointed Director of the Oblate Scholastics at Ampitiya by the then Oblate Provincial Fr. Anselm Silva, that I came to know Fr. Aloy more closely. Knowing well his expertise in matters spiritual, theological, Indological and pastoral, and with the collaborative spirit of my companion-formators, our Oblate Scholastics were sent to Tulana, the Research and Encounter Centre, Kelaniya, of which he is the Founder-Director, for ‘exposure-programmes’ on matters spiritual, biblical, theological and pastoral. Some of these dimensions according to my view and that of my companion-formators, were not available at the National Seminary, Ampitiya.
Ever since that time, our Oblate formators/ accompaniers at the Oblate Scholasticate, Ampitiya , have continued to send our Oblate Scholastics to Tulana Centre for deepening their insights and convictions regarding matters needed to serve the people in today’s context. Fr. Aloy also had tried very enthusiastically with the Oblate team headed by Frs. Oswald Firth and Clement Waidyasekara to begin a Theologate, directed by the Religious Congregations in Sri Lanka, for the contextual formation/ accompaniment of their members. It should very well be a desired goal of the Leaders / Provincials of the Religious Congregations.
Besides being a formator/accompanier at the Oblate Scholasticate, I was entrusted also with the task of editing and publishing our Oblate journal, ‘The Missionary Oblate’. To maintain the quality of the journal I continue to depend on Fr. Aloy for his thought-provoking and stimulating articles on Biblical Spirituality, Biblical Theology and Ecclesiology. I am very grateful to him for his generous assistance. Of late, his writings on renewal of the Church, initiated by Pope St. John XX111 and continued by Pope Francis through the Synodal path, published in our Oblate journal, enable our readers to focus their attention also on the needed renewal in the Catholic Church in Sri Lanka. Fr. Aloy appreciated very much the Synodal path adopted by the Jesuit Pope Francis for the renewal of the Church, rooted very much on prayerful discernment. In my Religious and presbyteral life, Fr.Aloy continues to be my spiritual animator / guide and ongoing formator / acccompanier.
Fr. Aloysius Pieris, BA Hons (Lond), LPh (SHC, India), STL (PFT, Naples), PhD (SLU/VC), ThD (Tilburg), D.Ltt (KU), has been one of the eminent Asian theologians well recognized internationally and one who has lectured and held visiting chairs in many universities both in the West and in the East. Many members of Religious Congregations from Asian countries have benefited from his lectures and guidance in the East Asian Pastoral Institute (EAPI) in Manila, Philippines. He had been a Theologian consulted by the Federation of Asian Bishops’ Conferences for many years. During his professorship at the Gregorian University in Rome, he was called to be a member of a special group of advisers on other religions consulted by Pope Paul VI.
Fr. Aloy is the author of more than 30 books and well over 500 Research Papers. Some of his books and articles have been translated and published in several countries. Among those books, one can find the following: 1) The Genesis of an Asian Theology of Liberation (An Autobiographical Excursus on the Art of Theologising in Asia, 2) An Asian Theology of Liberation, 3) Providential Timeliness of Vatican 11 (a long-overdue halt to a scandalous millennium, 4) Give Vatican 11 a chance, 5) Leadership in the Church, 6) Relishing our faith in working for justice (Themes for study and discussion), 7) A Message meant mainly, not exclusively for Jesuits (Background information necessary for helping Francis renew the Church), 8) Lent in Lanka (Reflections and Resolutions, 9) Love meets wisdom (A Christian Experience of Buddhism, 10) Fire and Water 11) God’s Reign for God’s poor, 12) Our Unhiddden Agenda (How we Jesuits work, pray and form our men). He is also the Editor of two journals, Vagdevi, Journal of Religious Reflection and Dialogue, New Series.
Fr. Aloy has a BA in Pali and Sanskrit from the University of London and a Ph.D in Buddhist Philosophy from the University of Sri Lankan, Vidyodaya Campus. On Nov. 23, 2019, he was awarded the prestigious honorary Doctorate of Literature (D.Litt) by the Chancellor of the University of Kelaniya, the Most Venerable Welamitiyawe Dharmakirthi Sri Kusala Dhamma Thera.
Fr. Aloy continues to be a promoter of Gospel values and virtues. Justice as a constitutive dimension of love and social concern for the downtrodden masses are very much noted in his life and work. He had very much appreciated the commitment of the late Fr. Joseph (Joe) Fernando, the National Director of the Social and Economic Centre (SEDEC) for the poor.
In Sri Lanka, a few religious Congregations – the Good Shepherd Sisters, the Christian Brothers, the Marist Brothers and the Oblates – have invited him to animate their members especially during their Provincial Congresses, Chapters and International Conferences. The mainline Christian Churches also have sought his advice and followed his seminars. I, for one, regret very much, that the Sri Lankan authorities of the Catholic Church –today’s Hierarchy—- have not sought Fr.
Aloy’s expertise for the renewal of the Catholic Church in Sri Lanka and thus have not benefited from the immense store of wisdom and insight that he can offer to our local Church while the Sri Lankan bishops who governed the Catholic church in the immediate aftermath of the Second Vatican Council (Edmund Fernando OMI, Anthony de Saram, Leo Nanayakkara OSB, Frank Marcus Fernando, Paul Perera,) visited him and consulted him on many matters. Among the Tamil Bishops, Bishop Rayappu Joseph was keeping close contact with him and Bishop J. Deogupillai hosted him and his team visiting him after the horrible Black July massacre of Tamils.
Features
A fairy tale, success or debacle

Sri Lanka-Singapore Free Trade Agreement
By Gomi Senadhira
senadhiragomi@gmail.com
“You might tell fairy tales, but the progress of a country cannot be achieved through such narratives. A country cannot be developed by making false promises. The country moved backward because of the electoral promises made by political parties throughout time. We have witnessed that the ultimate result of this is the country becoming bankrupt. Unfortunately, many segments of the population have not come to realize this yet.” – President Ranil Wickremesinghe, 2024 Budget speech
Any Sri Lankan would agree with the above words of President Wickremesinghe on the false promises our politicians and officials make and the fairy tales they narrate which bankrupted this country. So, to understand this, let’s look at one such fairy tale with lots of false promises; Ranil Wickremesinghe’s greatest achievement in the area of international trade and investment promotion during the Yahapalana period, Sri Lanka-Singapore Free Trade Agreement (SLSFTA).
It is appropriate and timely to do it now as Finance Minister Wickremesinghe has just presented to parliament a bill on the National Policy on Economic Transformation which includes the establishment of an Office for International Trade and the Sri Lanka Institute of Economics and International Trade.
Was SLSFTA a “Cleverly negotiated Free Trade Agreement” as stated by the (former) Minister of Development Strategies and International Trade Malik Samarawickrama during the Parliamentary Debate on the SLSFTA in July 2018, or a colossal blunder covered up with lies, false promises, and fairy tales? After SLSFTA was signed there were a number of fairy tales published on this agreement by the Ministry of Development Strategies and International, Institute of Policy Studies, and others.
However, for this article, I would like to limit my comments to the speech by Minister Samarawickrama during the Parliamentary Debate, and the two most important areas in the agreement which were covered up with lies, fairy tales, and false promises, namely: revenue loss for Sri Lanka and Investment from Singapore. On the other important area, “Waste products dumping” I do not want to comment here as I have written extensively on the issue.
1. The revenue loss
During the Parliamentary Debate in July 2018, Minister Samarawickrama stated “…. let me reiterate that this FTA with Singapore has been very cleverly negotiated by us…. The liberalisation programme under this FTA has been carefully designed to have the least impact on domestic industry and revenue collection. We have included all revenue sensitive items in the negative list of items which will not be subject to removal of tariff. Therefore, 97.8% revenue from Customs duty is protected. Our tariff liberalisation will take place over a period of 12-15 years! In fact, the revenue earned through tariffs on goods imported from Singapore last year was Rs. 35 billion.
The revenue loss for over the next 15 years due to the FTA is only Rs. 733 million– which when annualised, on average, is just Rs. 51 million. That is just 0.14% per year! So anyone who claims the Singapore FTA causes revenue loss to the Government cannot do basic arithmetic! Mr. Speaker, in conclusion, I call on my fellow members of this House – don’t mislead the public with baseless criticism that is not grounded in facts. Don’t look at petty politics and use these issues for your own political survival.”
I was surprised to read the minister’s speech because an article published in January 2018 in “The Straits Times“, based on information released by the Singaporean Negotiators stated, “…. With the FTA, tariff savings for Singapore exports are estimated to hit $10 million annually“.
As the annual tariff savings (that is the revenue loss for Sri Lanka) calculated by the Singaporean Negotiators, Singaporean $ 10 million (Sri Lankan rupees 1,200 million in 2018) was way above the rupees’ 733 million revenue loss for 15 years estimated by the Sri Lankan negotiators, it was clear to any observer that one of the parties to the agreement had not done the basic arithmetic!
Six years later, according to a report published by “The Morning” newspaper, speaking at the Committee on Public Finance (COPF) on 7th May 2024, Mr Samarawickrama’s chief trade negotiator K.J. Weerasinghehad had admitted “…. that forecasted revenue loss for the Government of Sri Lanka through the Singapore FTA is Rs. 450 million in 2023 and Rs. 1.3 billion in 2024.”
If these numbers are correct, as tariff liberalisation under the SLSFTA has just started, we will pass Rs 2 billion very soon. Then, the question is how Sri Lanka’s trade negotiators made such a colossal blunder. Didn’t they do their basic arithmetic? If they didn’t know how to do basic arithmetic they should have at least done their basic readings. For example, the headline of the article published in The Straits Times in January 2018 was “Singapore, Sri Lanka sign FTA, annual savings of $10m expected”.
Anyway, as Sri Lanka’s chief negotiator reiterated at the COPF meeting that “…. since 99% of the tariffs in Singapore have zero rates of duty, Sri Lanka has agreed on 80% tariff liberalisation over a period of 15 years while expecting Singapore investments to address the imbalance in trade,” let’s turn towards investment.
Investment from Singapore
In July 2018, speaking during the Parliamentary Debate on the FTA this is what Minister Malik Samarawickrama stated on investment from Singapore, “Already, thanks to this FTA, in just the past two-and-a-half months since the agreement came into effect we have received a proposal from Singapore for investment amounting to $ 14.8 billion in an oil refinery for export of petroleum products. In addition, we have proposals for a steel manufacturing plant for exports ($ 1 billion investment), flour milling plant ($ 50 million), sugar refinery ($ 200 million). This adds up to more than $ 16.05 billion in the pipeline on these projects alone.
And all of these projects will create thousands of more jobs for our people. In principle approval has already been granted by the BOI and the investors are awaiting the release of land the environmental approvals to commence the project.
I request the Opposition and those with vested interests to change their narrow-minded thinking and join us to develop our country. We must always look at what is best for the whole community, not just the few who may oppose. We owe it to our people to courageously take decisions that will change their lives for the better.”
According to the media report I quoted earlier, speaking at the Committee on Public Finance (COPF) Chief Negotiator Weerasinghe has admitted that Sri Lanka was not happy with overall Singapore investments that have come in the past few years in return for the trade liberalisation under the Singapore-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement. He has added that between 2021 and 2023 the total investment from Singapore had been around $162 million!
What happened to those projects worth $16 billion negotiated, thanks to the SLSFTA, in just the two-and-a-half months after the agreement came into effect and approved by the BOI? I do not know about the steel manufacturing plant for exports ($ 1 billion investment), flour milling plant ($ 50 million) and sugar refinery ($ 200 million).
However, story of the multibillion-dollar investment in the Petroleum Refinery unfolded in a manner that would qualify it as the best fairy tale with false promises presented by our politicians and the officials, prior to 2019 elections.
Though many Sri Lankans got to know, through the media which repeatedly highlighted a plethora of issues surrounding the project and the questionable credentials of the Singaporean investor, the construction work on the Mirrijiwela Oil Refinery along with the cement factory began on the24th of March 2019 with a bang and Minister Ranil Wickremesinghe and his ministers along with the foreign and local dignitaries laid the foundation stones.
That was few months before the 2019 Presidential elections. Inaugurating the construction work Prime Minister Ranil Wickremesinghe said the projects will create thousands of job opportunities in the area and surrounding districts.
The oil refinery, which was to be built over 200 acres of land, with the capacity to refine 200,000 barrels of crude oil per day, was to generate US$7 billion of exports and create 1,500 direct and 3,000 indirect jobs. The construction of the refinery was to be completed in 44 months. Four years later, in August 2023 the Cabinet of Ministers approved the proposal presented by President Ranil Wickremesinghe to cancel the agreement with the investors of the refinery as the project has not been implemented! Can they explain to the country how much money was wasted to produce that fairy tale?
It is obvious that the President, ministers, and officials had made huge blunders and had deliberately misled the public and the parliament on the revenue loss and potential investment from SLSFTA with fairy tales and false promises.
As the president himself said, a country cannot be developed by making false promises or with fairy tales and these false promises and fairy tales had bankrupted the country. “Unfortunately, many segments of the population have not come to realize this yet”.
(The writer, a specialist and an activist on trade and development issues . )












