Foreign News
Fears for Gazans as aid groups halt work over deadly Israeli strike
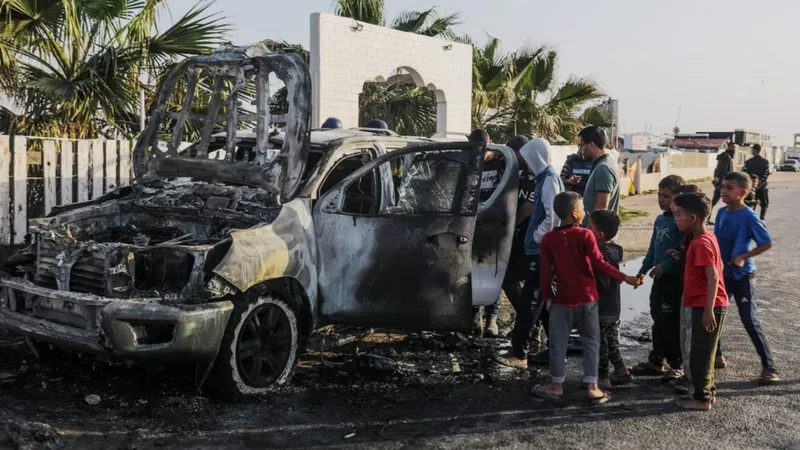

Many Palestinians in the Gaza Strip will be wondering how they are going to feed their families after World Central Kitchen (WCK) paused its operations in response to the killing of seven of its aid workers in an Israeli air strike.
Another US charity it works with, Anera, has also suspended work because of the escalating risks faced by its local staff and their families.
Together, they were serving two million meals a week across the Palestinian territory, where the UN has warned that an estimated 1.1 million people – half the population – are facing catastrophic hunger because of Israeli restrictions on aid deliveries, the ongoing hostilities and the breakdown of order.
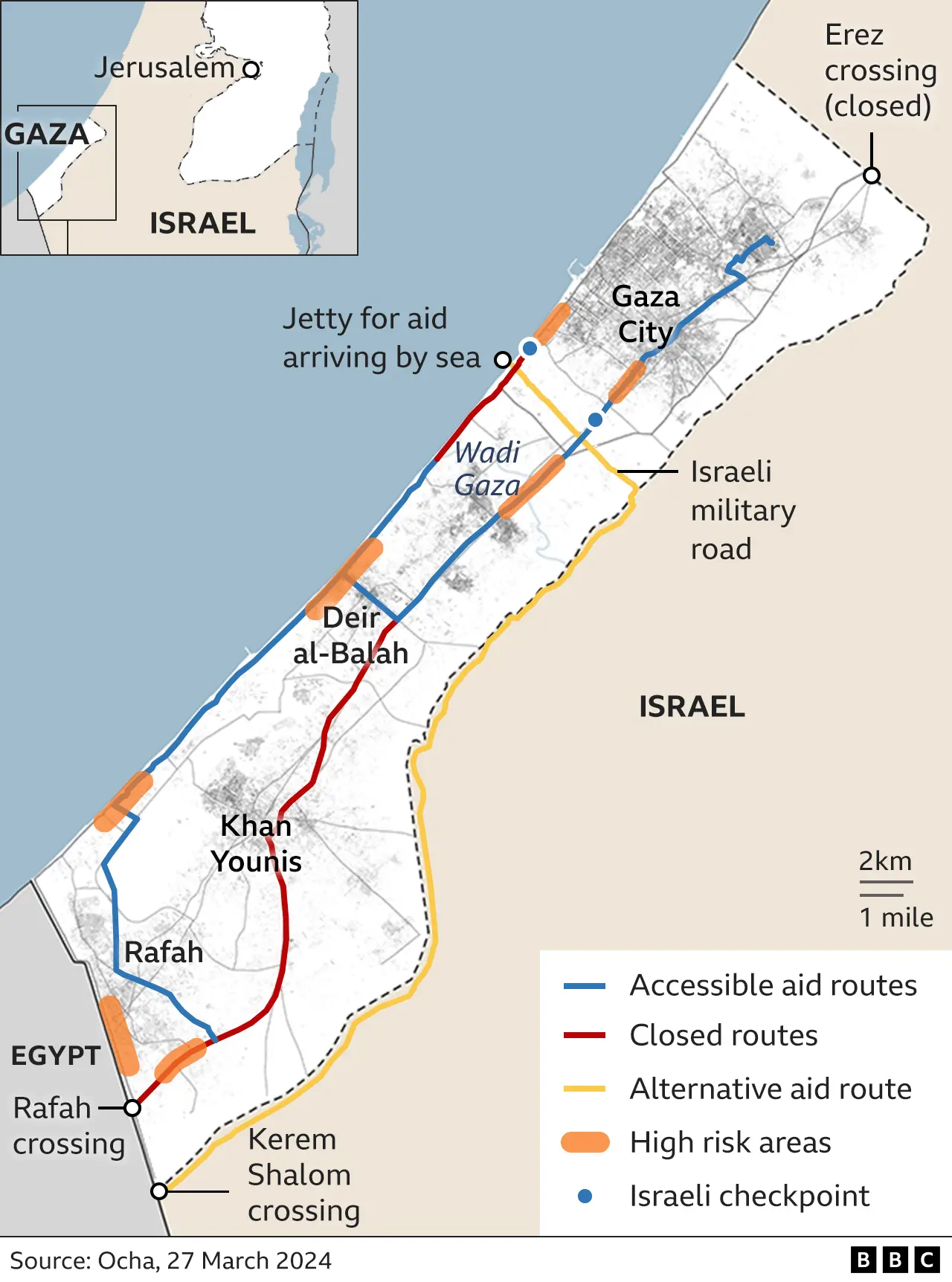
WCK’s decision to pause its work also led to the “freezing” of a maritime aid corridor from Cyprus, which the charity helped set up last month to increase the trickle of aid getting into the north of Gaza and avert a looming famine.
The WCK convoy was hit on Monday night as it travelled south along the Israeli-designated coastal aid route, just after they had unloaded more than 100 tonnes of food from a barge at a warehouse in Deir al-Balah.
That barge was part of a four-vessel flotilla that sailed back to Cyprus with 240 tonnes of supplies that could not be brought ashore in the wake of the strike.
The Norwegian Refugee Council warned that “what happened to World Central Kitchen threatens the entire aid system” and had left it “on the brink”.

Before the strike, World Central Kitchen was providing about 350,000 meals across Gaza each day
WCK accused the Israeli military of a “targeted attack” on vehicles clearly marked with the charity’s logo and whose movements had been co-ordinated with Israel authorities. The victims were British, Polish, Australian and Palestinian, and also included a dual US-Canadian citizen.
The military’s chief of staff, Lt Gen Herzi Halevi, described the strike as a “grave mistake” that had followed “misidentification at night”.
He also vowed to take “immediate action” to ensure that more was done to protect aid workers, including the immediate establishment of a new “humanitarian command centre” to improve co-ordination. “Israel is at war with Hamas, not with the people of Gaza,” he stressed.
However, aid groups say they are not sure such promises will lead to meaningful changes. They also assert that this was not an isolated incident, with 196 Palestinian aid workers reportedly killed since the war began in October.
Jan Egeland, the secretary-general of the Norwegian Refugee Council and a former UN humanitarian chief, told the BBC that WCK was “among those who have the closest co-operation with the Israelis”, in terms of sharing information about their workers’ locations and planned movements.
Before the strike, WCK was playing an increasingly prominent and important role in Gaza, with 400 Palestinian staff and 3,000 people working indirectly in its 68 community kitchens and distribution system across the territory.
WCK provided 12% of the 193,000 tonnes of aid from international organisations that had reached Gaza as of Tuesday, according to data from Cogat, the Israeli defence ministry body tasked with co-ordinating deliveries. However, UN agencies were responsible for 80% of the total.
WCK’s founder, the chef José Andrés, told Reuters news agency on Wednesday that it was “analysing the situation and how to keep doing the work we do”.
Anera – which was providing 150,000 meals a day in collaboration with WCK – said it understood the consequences pausing its own work would have on Palestinians, but that its Palestinian staff had for the first time deemed the risk to their safety and that of their families “intolerable”.
It said the charity’s logistics co-ordinator and his son had been killed in an Israeli air strike in Deir al-Balah in March, despite the fact that the co-ordinates of the shelter where they were staying had been provided to the Israeli military. “We’ve asked for explanation as to why that site was struck and we’ve received none,” Derek Madsen of Anera told the BBC. “These sites are known and so I think it is very difficult for us to understand how these strikes happen.”
For the people of Gaza, the suspension of WCK’s operations “means more famine, more dead children, more epidemic disease because people are so malnourished”, Mr Egeland warned.
At least 27 children are reported to have died as a result of malnutrition since October, according to the World Health Organization.
Mr Egeland urged Israel to start by opening the Karni and Erez border crossings with northern Gaza to allow aid convoys to drive there directly.
Most aid convoys are currently forced to start at the Israeli-controlled Kerem Shalom and Egyptian-controlled Rafah crossings with the south of Gaza and then pass through what the UN calls “high-risk areas”, mainly due to shooting and shelling or the breakdown in civil order.

The Open Arms. a Spanish charity vessel, returned to Cyprus on Wednesday after the maritime aid route was suspended (BBC)
Cogat says Israeli forces have co-ordinated the entry of more than 500 lorries into the north over the past two months via those routes as well as a new gate and military road that runs south of Gaza City.
Israel has also facilitated the now-suspended maritime corridor set up by WCK as well as airdrops of aid by Western and Arab countries, which the UN says are both helpful but cannot replace the large-scale delivery of aid by land.
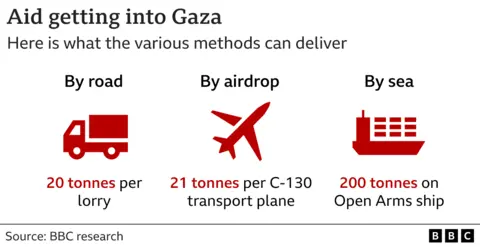
The first WCK aid ship was carrying 200 tonnes of aid and took several days to reach Gaza. By comparison, a lorry can carry about 20 tonnes and the nearest Israeli container port is only a 40km drive from northern Gaza.
A C-130 transport plane meanwhile has a maximum payload of 21 tonnes, but only about 40 airdrops have taken place so far and they are considered expensive, ineffective and dangerous for people on the ground.
The UN says 159 lorry loads of aid crossed into Gaza by land each day on average between 1 and 28 March, and that the pre-war average was 500 lorry loads, including fuel.
Cogat says the pre-war average only included 70 food lorries and that 140 entered each day during March. It insists there is no limit to the amount of food and other humanitarian aid that can enter Gaza and accuses UN agencies of failing to distribute aid effectively.
There was no apparent drop-off in aid crossing into Gaza following the strike on the WCK convoy, with 217 lorries transferred via Israel and Egypt on Wednesday and 179 food packages being airdropped, according to Cogat.
But Nate Mook, who was chief executive of WCK until 2022, warned that the longer-term consequences could be “devastating” for Gazans because “we probably have not seen the last of the aid organisations to pull out”.
Aseel Baidoun of Medical Aid for Palestinians said it had not suspended operations after a strike in January damaged a residential compound that housed the British charity’s local team and their families, injuring several people. But now, she added: “We really are scared of the security situation.”
Natalia Anguera of Action Against Hunger told the BBC that it would try to continue working despite “more and more challenging” conditions.
“Most of our staff are… Palestinians. They are suffering themselves, but they also have a very strong and clear commitment to their humanitarian mandate. They want to go on delivering,” she said.
She said the international community needed to push strongly for a humanitarian ceasefire because it was the only way that aid organisations would be able to scale up their response to the level required.
Mr Egeland also stressed the importance of the UN agency for Palestinian refugees (UNRWA), which he said was “bigger than the rest of us combined” but was being “systematically undermined by Israel”.
Israel accuses UNRWA of supporting Hamas, which triggered the war when its gunmen attacked southern Israel on 7 October last year. The agency has denied this, but in January it sacked nine of the 12 employees accused in an Israeli document of playing a part in the attacks.
UNRWA called for a “complete reversal in policies” from Israel in response to Monday’s strike, including lifting the ban on it delivering aid to northern Gaza.
(BBC)
Foreign News
Nasa ‘Earthrise’ astronaut dies at 90 in plane crash

Apollo 8 astronaut Bill Anders, who snapped one of the most famous photographs taken in outer space, has died at the age of 90.
Officials say a small plane he was flying crashed into the water north of Seattle, Washington.
Anders’ son Greg confirmed that his father was flying the small plane, and that his body was recovered on Friday afternoon. “The family is devastated. He was a great pilot. He will be missed,” a statement from the family reads.
Anders – who was a lunar module pilot on the Apollo 8 mission – took the iconic Earthrise photograph, one of the most memorable and inspirational images of Earth from space.
Taken on Christmas Eve during the 1968 mission, the first crewed space flight to leave Earth and reach the Moon, the picture shows the planet rising above the horizon from the barren lunar surface.
Anders later described it as his most significant contribution to the space programme.

The image is widely credited with motivating the global environmental movement and leading to the creation of Earth Day, an annual event to promote activism and awareness of caring for the planet.
Speaking of the moment, Anders said: “We came all this way to explore the Moon, and the most important thing that we discovered was the Earth.”
Officials said on Friday that Anders crashed his plane around 11:40PDT (1940BST).
The US National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) said the 90-year-old was flying a Beechcraft A A 45 – also known as a T-34. The agency said that the plane crashed about 80ft (25m) from the coast of Jones Island.
Anders also served as the backup pilot to the Apollo 11 mission, the name of the effort that led to the first Moon landing on July 24, 1969.
Following Anders’ retirement from the space programme in 1969, the former astronaut largely worked in the aerospace industry for several decades. He also served as US Ambassador to Norway for a year in the 1970s.
But he is best remembered for the Apollo 8 mission and the iconic photograph he took from space.
“In 1968, during Apollo 8, Bill Anders offered to humanity among the deepest of gifts an astronaut can give. He traveled to the threshold of the Moon and helped all of us see something else: ourselves,” Nasa Administrator Bill Nelson said in a statement.
Mark Kelly, a former astronaut who now serves as a US Senator for the state of Arizona, said in a post on X, formerly Twitter, that Anders “inspired me and generations of astronauts and explorers. My thoughts are with his family and friends”.
[BBC]
Foreign News
China’s Chang’e-6 lifts off from far side of Moon with rock samples

A Chinese spacecraft carrying rock and soil samples from the far side of the Moon has lifted off from the lunar surface to start its journey back to Earth, according to state media.
The achievement on Tuesday is a world first and the latest leap for Beijing’s decades-old space programme, which aims to send a crewed mission to the Moon by 2030.
The Xinhua News Agency, citing the China National Space Administration (CNSA), said that the ascender of the Chang’e-6 probe took off at 7:38am local time on Tuesday (23:38 GMT) and entered a preset orbit around the moon.
It described the move as “an unprecedented feat in human lunar exploration history”.
The Chang’e-6 probe was launched last month and its lander touched down on the far side of the Moon on Sunday. It used a drill and robotic arm to dig up soil on and below the Moon’s surface, according to Xinhua.
After successfully gathering its samples, the Chang’e-6 unfurled China’s national flag for the first time on the far side of the Moon, it said.
The agency cited the CNSA as saying that the spacecraft stowed the samples it had gathered in a container inside the ascender of the probe as planned.
[Aljazeera]
Foreign News
China says its spacecraft lands on Moon’s far side

China says its uncrewed craft has successfully landed on the far side of the Moon – an unexplored place almost no-one tries to go.
The Chang’e 6 touched down in the South Pole-Aitken Basin at 06:23 Beijing time on Sunday morning (22:23 GMT Saturday), the China National Space Administration (CNSA) said.
Launched on 3 May, the mission aims to collect precious rock and soil from this region for the first time in history. The probe could extract some of the Moon’s oldest rocks from a huge crater on its South Pole.
The landing was fraught with risks, because it is very difficult to communicate with spacecraft once they reach the far side of the Moon. China is the only country to have achieved the feat before, landing its Chang’e-4 in 2019.
After launching from Wenchang Space Launch Center, the Chang’e 6 spacecraft had been orbiting the Moon waiting to land. The lander component of the mission then separated from the orbiter to touch down on the side of the Moon that faces permanently away from Earth.
During the descent, an autonomous visual obstacle avoidance system was used to automatically detect obstacles, with a visible light camera selecting a comparatively safe landing area based on the brightness and darkness of the lunar surface, the CNSA was quoted as saying by state-run Xinhua news agency.
The lander hovered about 100m (328ft) above the safe landing area, and used a laser 3D scanner before a slow vertical descent. The operation was supported by the Queqiao-2 relay satellite, the CNSA said.
Chinese state media described the successful landing as an “historic moment”. The state broadcaster said “applause erupted at the Beijing Aerospace Flight Control Center” when the Chang’e landing craft touched down on the Moon early on Sunday morning.
The lander should spend up to three days gathering materials from the surface in an operation the CNSA said would involve “many engineering innovations, high risks and great difficulty”. “Everyone is very excited that we might get a look at these rocks no-one has ever seen before,” explains Professor John Pernet-Fisher, who specialises in lunar geology at the University of Manchester.
He has analysed other lunar rock brought back on the American Apollo mission and previous Chinese missions. But he says the chance to analyse rock from a completely different area of the Moon could answer fundamental questions about how planets form.
Most of the rocks collected so far are volcanic, similar to what we might find in Iceland or Hawaii. But the material on the far side would have a different chemistry . “It would help us answer those really big questions, like how are planets formed, why do crusts form, what is the origin of water in the solar system?” the professor says.
The mission aims to collect about 2kg (4.4lb) of material using a drill and mechanical arm, according to the CNSA.
The South Pole–Aitken basin, an impact crater, is one of the largest known in the solar system.
From there, the probe could gather material that came from deep inside the lunar mantle – the inner core of the Moon – Prof Pernet-Fisher says.
The Moon’s South Pole is the next frontier in lunar missions – countries are keen to understand the region because there is a good chance it has ice.

The capsule in the last Chinese moon mission, Chang’e 5, brought back soil and rocks in 2020 (BBC)
Access to water would significantly boost the chances of successfully establishing a human base on the Moon for scientific research.
If the mission succeeds, the craft will return to Earth with the precious samples on board a special return capsule.
The material will be kept in special conditions to try to keep it as pristine as possible.
Scientists in China will be given the first chance to analyse the rocks, and later researchers around the world will be able to apply for the opportunity too.
This is the second time China has launched a mission to collect samples from the Moon.
In 2020 Chang’e 5 brought back 1.7kg of material from an area called Oceanus Procellarum on the Moon’s near side.
China is planning three more uncrewed missions this decade as it looks for water on the Moon and investigates setting up a permanent base there.
Beijing’s broader strategy aims to see a Chinese astronaut walk on the moon by around 2030.
The US also aims to put astronauts back on the moon, with Nasa aiming to launch its Artemis 3 mission in 2026.
(BBC)
























