Business
Battling Disease and Debt: Financing Non-Communicable Diseases amidst Sri Lanka’s economic crisis
By Sunimalee Madurawala
“The shortage of medicines will significantly impact medications for non-communicable diseases (NCDs). If NCD patients don’t receive their regular medication, their condition will worsen,” stated a Provincial Director of Health Services speaking on the implications of the economic crisis on NCDs. Over the last few decades, NCDs have emerged as a critical health challenge for Sri Lanka, placing a significant burden on the country’s healthcare system. More than 80 % of the total deaths that occurred in the country are due to NCDs. NCDs accounted for 38% of the country’s total health expenditure in 2019, amounting to USD 1,183 million. The economic impact is particularly challenging for households affected by chronic NCDs as they bear higher costs of medicines, pharmaceutical products, medical laboratory tests, and other ancillary services. With the current economic downturn, preventing and financing NCDs has become even more challenging for Sri Lanka.
An ongoing IPS study delves into the implications of the economic crisis on the country’s health system, with a specific focus on NCD prevention and financing. The study conducted an extensive analysis by gathering perspectives from various stakeholders. This blog is based on the information collected from these stakeholders.
Economic Crisis and Sri Lanka’s Health System
The COVID-19 pandemic has already put Sri Lanka’s health sector under intense pressure, and the ongoing economic crisis has added more stress to the sustainability of the country’s healthcare system. An economic crisis can directly and indirectly impact a health system. For instance, during times of economic crisis, it’s common for governments to reduce their social expenditures, and one area that could be affected is healthcare. This could result in cuts to health budgets. Furthermore, the demand for healthcare services will decrease, particularly in the private sector, where treatment costs could increase. Additionally, child and maternal nutrition and other health outcomes will deteriorate as with the increasing food prices, people opt to reduce food quantity and quality.
Once well-recognised for its strength and cost-effectiveness, Sri Lanka’s health system is now challenged by knowledge, capacity, and policy gaps. The economic crisis would undoubtedly worsen these gaps, even to the point of the collapse of the health system. The adverse impacts of the economic crisis could hinder the laudable progress achieved by the country over the years, leading to an increase in NCDs, malnutrition among children, communicable diseases, and mental health issues.
Implications on NCDs
The economic crisis in Sri Lanka has significant short-term and long-term implications for NCD prevention and financing. In the short term, the shortage of medical supplies has become the most pressing concern. Further, resource limitations have resulted in the delay or limitation of lab tests and surgeries, including non-essential and non-urgent surgeries at government hospitals. In addition, the fuel shortage which escalated last year has severely impacted preventive care services, curative care services, and administrative functions at all levels of the health sector, weakening the entire health delivery mechanism. Moreover, the government’s decision to limit capital expenditure would have serious negative repercussions on maintaining the existing NCD service delivery and catering to the increasing demand for NCD preventive (e.g., awareness campaigns and screening programmes) and curative (e.g., construction of hospitals and clinics) measures in the future.
Participating in one of our interviews, an officer from a Provincial Health Ministry stated that, in the long term,” the prevalence of risk factors will undoubtedly increase eventually, and individuals who already suffer from NCDs may find it challenging to manage their conditions.” For example, the prevalence of unhealthy dietary patterns – one of the NCD behavioural risk factors – is likely to become more prevalent. Even before the economic crisis, Sri Lanka’s nutrition indicators stood at a lower level and there was limited progress towards achieving the diet-related non-NCD targets. The high food prices have compelled people to either reduce or avoid consuming healthy foods or opt for cheap, unhealthy foods. This would “lead to a decline in earning and learning capacities for the next generation resulting in generational effects”, feared a Provincial Health Ministry officer.
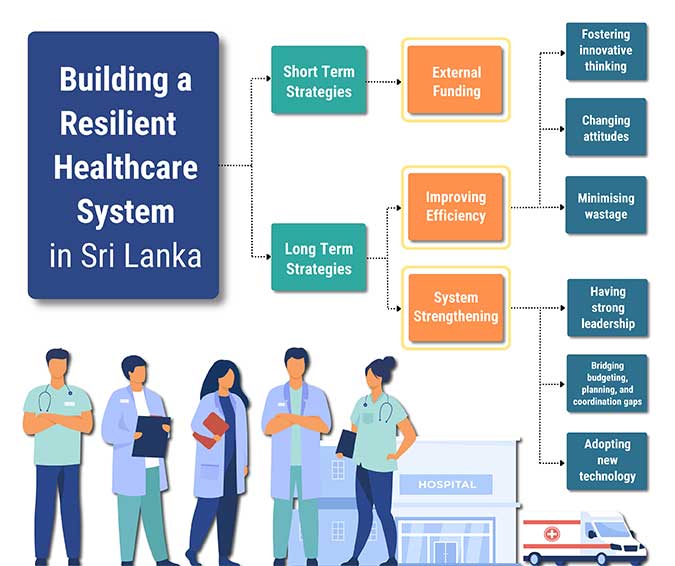
Becoming More Resilient and Facing the Challenges – the Way Forward
Most stakeholders who participated in this study suggested that seeking external funding is the most suitable short-term strategy for Sri Lanka to finance NCDs to overcome the current crisis. “We (the country) should also aim to receive more foreign aid instead of loans, which requires close discussions with other countries and international organisations suggested a senior officer from the Ministry of Health.
While seeking external support as a short-term relief, it is crucial to focus on long-term strategies to improve the resilience of Sri Lanka’s healthcare system in handling future crises.Improving efficiency and strengthening the system are vital long-term strategies proposed by the stakeholders in building a more resilient healthcare system.
Minimising wastage, changing attitudes, and fostering innovative thinking should be the key pillars of increasing efficiency, as indicated by the stakeholders. Likewise, system strengthening requires strong leadership, the use of technology, and paying more attention to budgeting, planning, and coordination. Additionally, exploring alternative financing ventures, restructuring the health financing system, and focusing on smarter spending are necessary as providing citizens with free healthcare becomes increasingly challenging for the government in a limited fiscal space. Such measures would make the country’s healthcare system robust which can withstand both the short-term and long-term consequences of a crisis, assured the stakeholders who participated in this study.
Despite the severe impact of the current economic crisis on NCD prevention and financing efforts, it provides an opportunity to understand the gaps in the existing system and develop a more sustainable and resilient healthcare system to cater to the increasing demand for NCD prevention and financing.
- This study is carried out in collaboration with the Center for Policy Impact in Global Health (CPIGH) of Duke University with financial support from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.

Link to blog: https://www.ips.lk/talkingeconomics/2023/04/20/battling-disease-and-debt-financing-non-communicable-diseases-amidst-sri-lankas-economic-crisis/
Sunimalee Madurawala is a Research Economist at IPS. Her research interests include health economics, gender and population studies. Sunimalee holds a BA (Economics Special) with First Class Honours and a Masters in Economics (MEcon) from the University of Colombo, Sri Lanka. (Talk to Sunimalee – sunimalee@ips.lk)
Business
AHK Sri Lanka champions first-ever Sri Lankan delegation at Drupa 2024

The Delegation of German Industry and Commerce in Sri Lanka (AHK Sri Lanka) proudly facilitated the first-ever Sri Lankan delegation’s participation at Drupa 2024, the world’s largest trade fair for the printing industry and technology. Held after an eight-year hiatus, Drupa 2024 was a landmark event, marking significant advancements and opportunities in the global printing industry.
AHK Sri Lanka played a pivotal role in organising and supporting the delegation, which comprised 17 members from the Sri Lanka Association for Printers (SLAP), representing eight companies from the commercial, newspaper, stationery printing, and packaging industries. This pioneering effort by AHK Sri Lanka not only showcased the diverse capabilities of Sri Lanka’s printing sector but also facilitated vital bilateral discussions with key stakeholders from the German printing industry.
Business
Unveiling Ayugiri: Browns Hotels & Resorts sets the stage for a new era in luxury Ayurveda Wellness

In a captivating reimagining of luxury wellness tourism, Browns Hotels & Resorts proudly unveiled the exquisite Ayugiri Ayurveda Wellness Resort Sigiriya. This momentous occasion, celebrated amidst a vibrant and serene grand opening on the 6th of June, heralds a new chapter in the Ayurveda wellness tourism landscape in Sri Lanka. Nestled amidst 54 acres of unspoiled natural splendour, Ayugiri features 22 exclusive suites and stands out as the only luxury Ayurveda wellness resort in the country offering plunge pools in every room, rendering it truly one-of-a-kind.
The grand opening of Ayugiri Ayurveda Wellness Resort was an enchanting event, where guests were captivated by the melodies of flutists and violinists resonating through Sigiriya’s lush landscapes. As traditional drummers and dancers infused the air with vibrant energy, Browns Hotels & Resorts’ CEO, Eksath Wijeratne, Kotaro Katsuki, Acting Ambassador for the Embassy of Japan and General Manager, Buwaneka Bandara, unveiled the resort’s new logo, marking a significant moment witnessed by distinguished guests from the French Embassy, Ayurveda and wellness enthusiasts along with officials from the Sigiriya area, LOLC Holdings and Browns Group.
“Our strategic expansion into wellness tourism with Ayugiri Ayurveda Wellness Resort Sigiriya symbolises a significant milestone for Browns Hotels & Resorts. Wellness tourism has consistently outperformed the overall tourism industry for over a decade, reflecting a growing global interest in travel that goes beyond leisure to offer rejuvenation and holistic well-being. By integrating the timeless wisdom of Ayurveda with modern luxury, we aim to set a new standard in luxury wellness tourism in Sri Lanka. Whether your goal is prevention, healing, or a deeper connection to inner harmony, Ayugiri offers a sanctuary for holistic well-being” stated Eksath Wijeratne.
Ayugiri encapsulates the essence of life, inspired by the lotus flower held by the graceful queens of the infamous Sigiriya frescoes. Just as the lotus emerges from the murky depths, untainted and serene,
Ayugiri invites guests on a journey of purity and rejuvenation, harmonised with a balance of mind, body and spirit, the essence of nature, echoes of culture and the wisdom of ancient Ayurvedic healing.
Business
HNB General Insurance recognized as Best General Bancassurance Provider in Sri Lanka 2024

HNB General Insurance, one of Sri Lanka’s leading general insurance providers, has been honored as the Best General Bancassurance Provider in Sri Lanka 2024 by the prestigious Global Banking and Finance Review – UK.
The esteemed accolade underscores HNB General Insurance’s unwavering commitment to excellence and its outstanding performance in the field of bancassurance. Through dedication and hard work, the HNB General Insurance team has continuously endeavored to deliver innovative insurance solutions, cultivate strong relationships with banking partners, and provide unparalleled service to customers nationwide. This recognition is a testament to the team’s dedication and relentless pursuit of excellence in the bancassurance business.
“We are honored to receive this prestigious award, which reflects our team’s tireless efforts and dedication to delivering value-added insurance solutions and exceptional service through our bancassurance partnerships,” said Sithumina Jayasundara, CEO of HNB General Insurance. “This recognition reaffirms our position as a trusted insurance provider in Sri Lanka and motivates us to continue striving for excellence in serving our customers and communities.”













